NXP and COMPREDICT together are bringing Edge AI to life in automotive applications.
COMPREDICT’s Virtual Sensors provide a smarter alternative to traditional hardware sensors. Trained on high-quality datasets, these AI models provide real-time estimates and are fully software driven. Not only are they scalable and cost-effective, but they also continuously improve through learning.
NXP’s S32 processors provide the ideal hardware foundation for Edge AI performance, with Arm® Cortex®cores for general processing, AI / ML accelerators for real-time inference and low-power design for embedded environments. Edge AI needs more than silicon—it needs purpose-built software. NXP’s eIQ ® Auto ML software development kit supports the full model pipeline: model preparation, optimization and deployment. This ensures models run efficiently on constrained automotive devices.
Start your Edge AI journey today request a demo, explore partnerships and unlock smarter, software-defined mobility with NXP Edge AI solutions.
This partnership simplifies Edge AI adoption and reduces vehicle bill of materials (BoM) costs, helping OEMs and Tier-1 suppliers jumpstart their journey toward smarter, software-driven mobility.
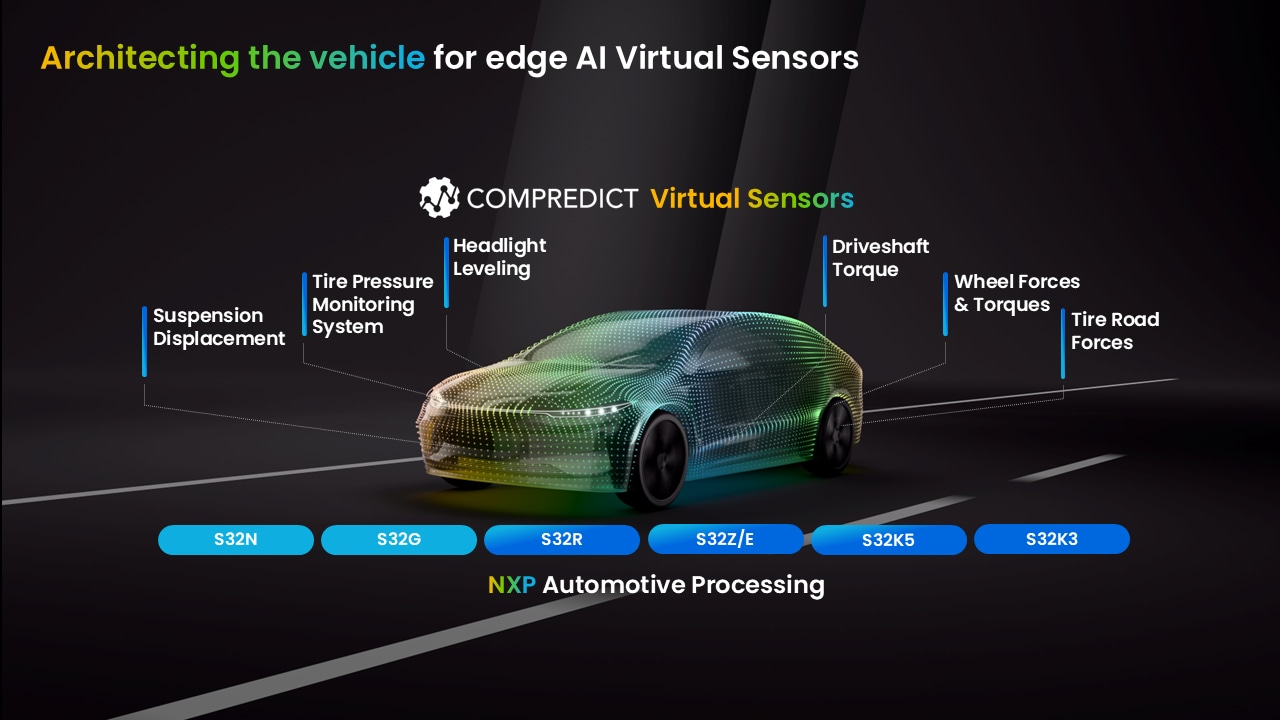 This illustration outlines COMPREDICT models supported by NXP’s S32 Automotive Processing
This illustration outlines COMPREDICT models supported by NXP’s S32 Automotive Processing
Wheel force transducers (WFTs) are essential for vehicle testing, capturing force and torque data to inform suspension tuning and safety validation. However, traditional WFTs are bulky, expensive and not suited for mass deployment.
For example, the AI-enhanced WFT solution: utilizing the NXP S32 networking portfolio, sensor data flows from the vehicle to NXP’s edge microprocessors and controllers. From there, COMPREDICT’s model delivers real-time force estimations and maintenance alerts. This combination is a game-changer for testing, autonomy and vehicle diagnostics. Complementing this solution, Synopsys’ virtual development kit (VDK) allows developers to deploy and test models on virtual hardware, accelerating integration and reducing risk without physical hardware required.
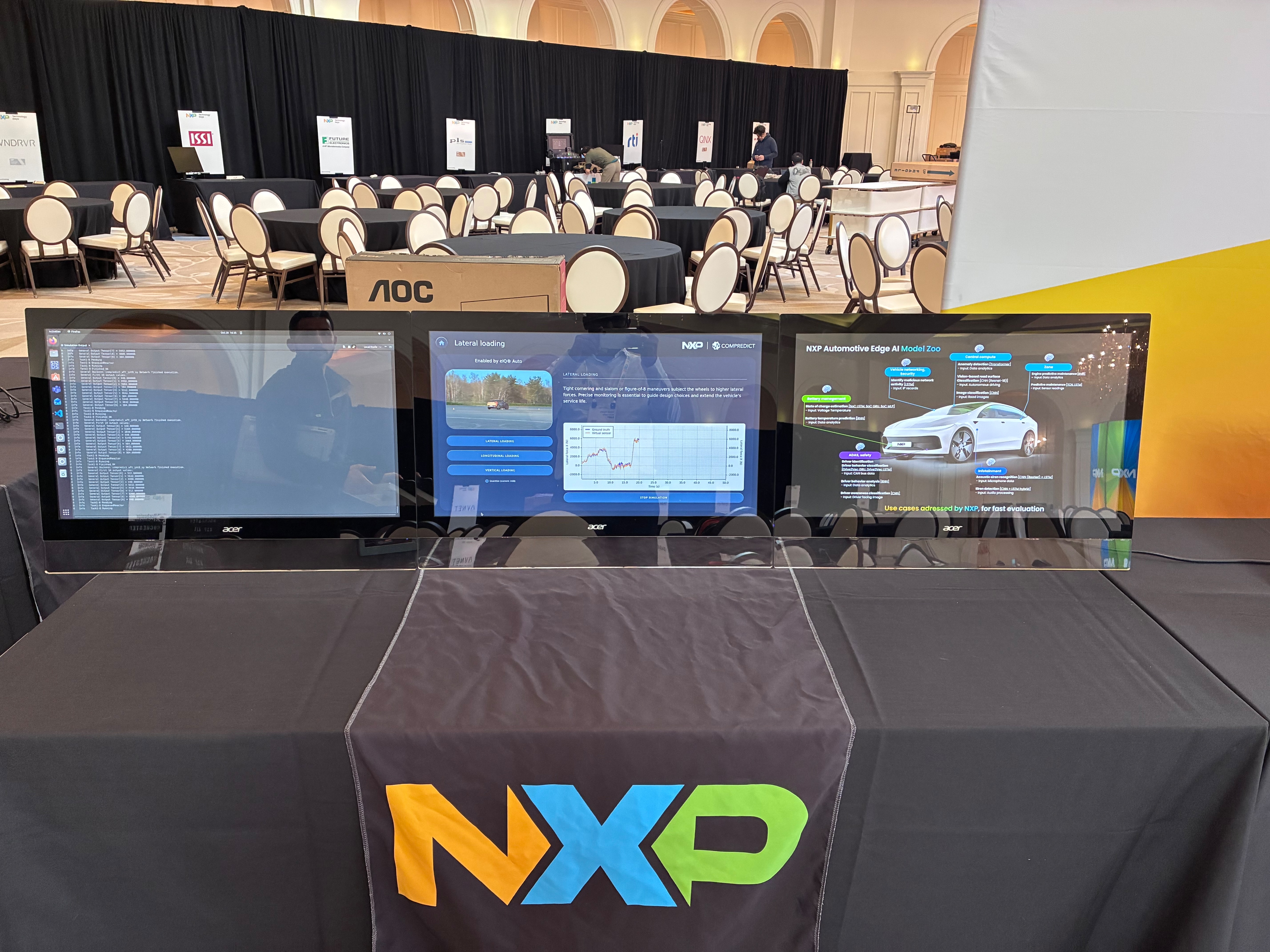 This photo features a live and in-person AI-Enhanced WFT Demonstration
This photo features a live and in-person AI-Enhanced WFT Demonstration
For OEMs and Tier-1 suppliers, this WFT solution represents a scalable, cost-effective path for integrating software-defined sensing across vehicle platforms. As the industry shifts toward software-defined vehicles (SDVs), NXP and COMPREDICT offer a future-ready approach to deploying AI—virtually, efficiently and at scale.
Use Case Deep Dive: AI-Enhanced WFT
The deployment of COMPREDICT’s Virtual Sensor model for WFT on NXP hardware was carried out using the NXP eIQ Auto software development environment. Starting from a trained model—originally in TensorFlow, but compatible with other popular frameworks like PyTorch, MATLAB, and various open-source options—we first compiled it with FP32 precision for the target Arm Cortex-R52 cores.
Initial execution involved Synopsys’ VDK, enabling pre-silicon validation. Using a dataset provided by COMPREDICT, the model then was quantized to 8-bit integer (INT8), significantly reducing its footprint while balancing inference accuracy. This optimization also prepares the model for deployment on the eIQ Neutron neural processing unit (NPU). Leveraging NXP’s eIQ Auto compiler and the S32K5 VDK, we successfully deployed the quantized model on the R52 core, demonstrating efficient Edge AI execution on a zonal microcontroller, precisely where this use case is intended for production.
 This photo features a live and in-person AI-Enhanced WFT Demonstration
This photo features a live and in-person AI-Enhanced WFT Demonstration
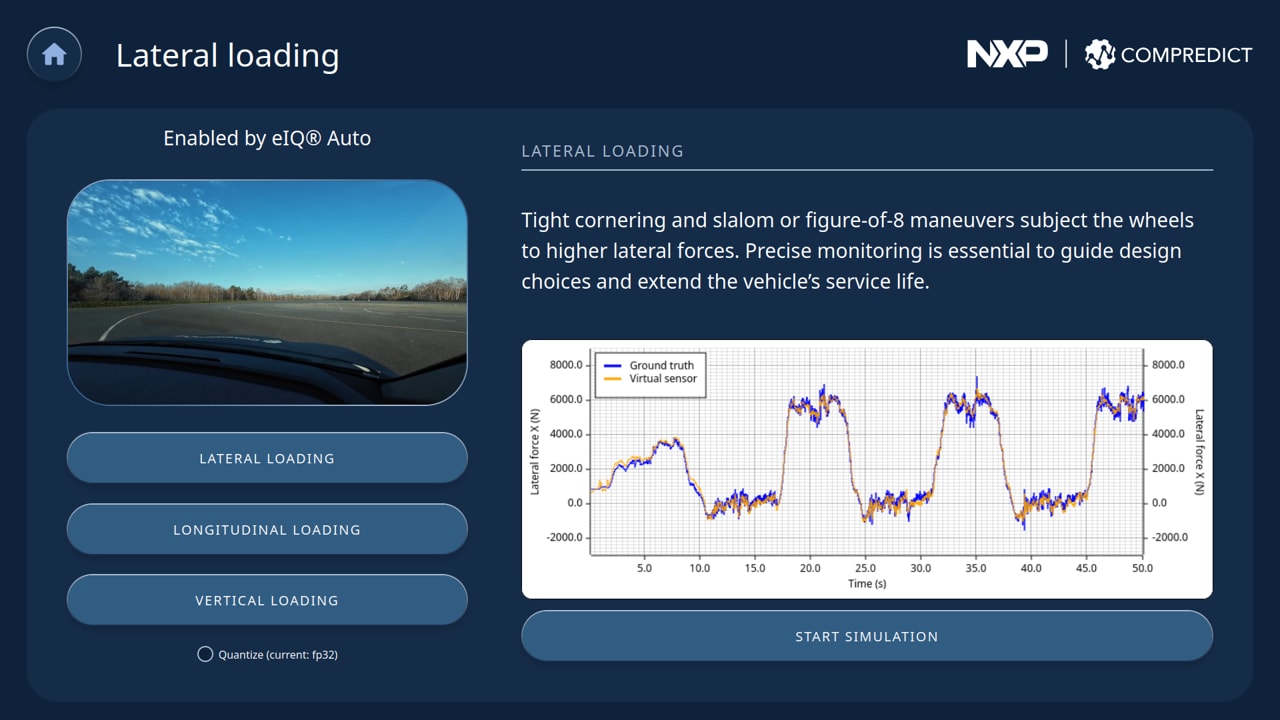
This use case was demonstrated across three real-time dynamic loading scenarios—lateral, longitudinal and vertical—where the force and torque data came from controller area network (CAN) signals (15 signals @ 25-100 Hz). In each case, the Virtual Sensor output was compared against the hardware sensor data, highlighting the outstanding performance of COMPREDICT’s WFT model.
What sets this solution apart is its:
- Adaptablity: Seamlessly integration with existing CAN bus architectures, minimizing changes to vehicle infrastructure.
- Comprehensive data coverage: Training on ∼3 hours of diverse driving scenarios, including city traffic, high-speed runs, potholes, slalom maneuvers and braking events.
- Series production ready: Bypassing of the limitations associated with traditional use of hardware-based WFT on public roads, making series-production vehicles as intelligent as advanced prototypes.
Start Your Edge AI Journey Today
Ready to explore the future of automotive intelligence?




