Getting Started with KW47-EVK
Contents of this document
-
Plug It In
-
Get Software
-
Build and Run
-
Create
-
MCUXpresso Developer Experience
Sign in to save your progress. Don't have an account? Create one.

Purchase your KW47-EVK
1. Plug It In
Let's take your KW47-EVK board for a test drive. In following the steps, you may either watch the sequence in a short video, or follow the detailed actions listed below.
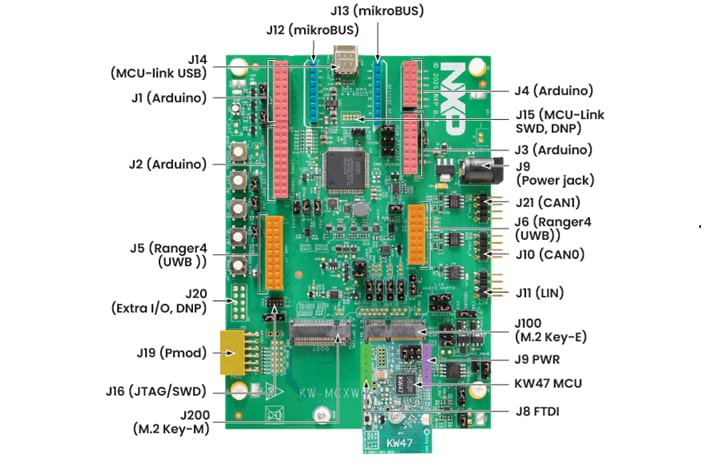
1.1 Get Familiar with the Board
The KW47-EVK board is preprogrammed with a wireless demo. This serves as a sanity check to verify that the device is working as expected, right out of the box.
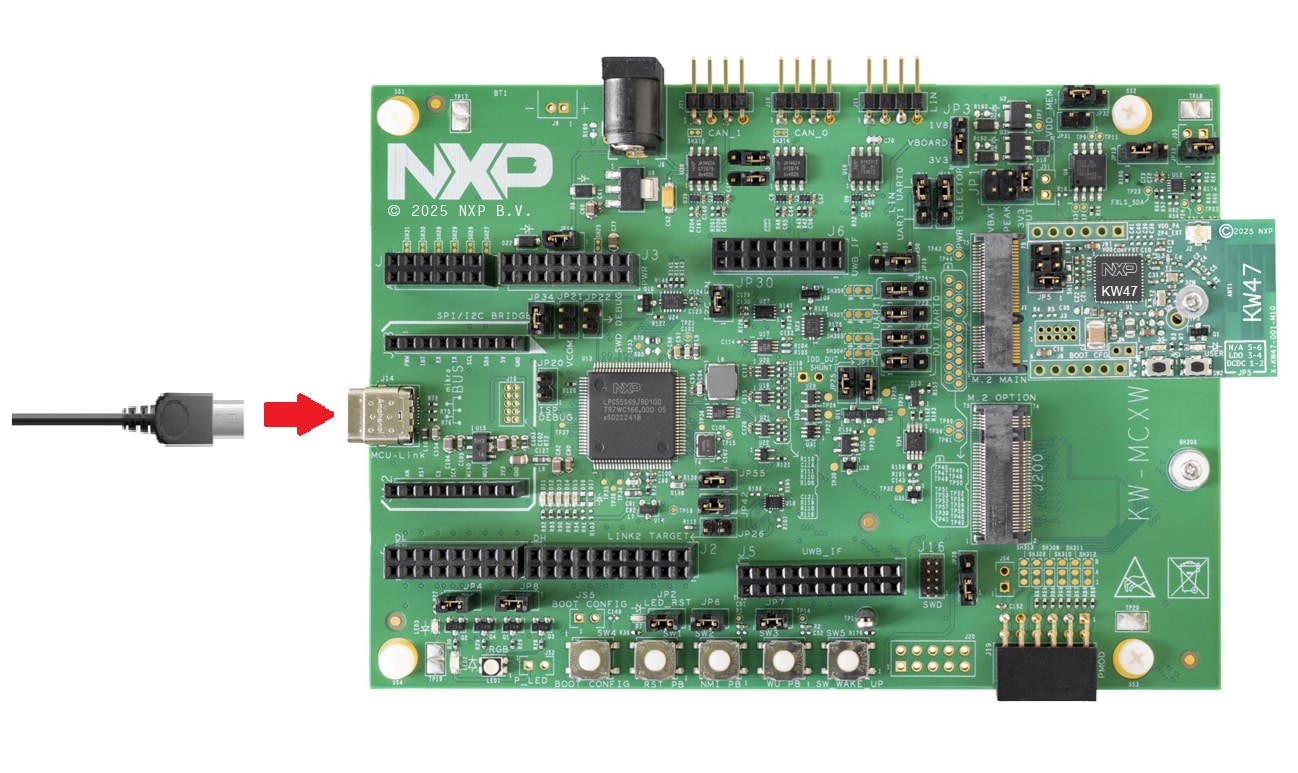
1.2 Plug In the Board
Connect a USB Type-C cable from the connector J14 to a host computer or power supply to power up the board and run the demo program. This demo can be tested with the NXP's IoT Toolbox app. For an out-of-the-box experience, please download the NXP's IoT Toolbox app on your smartphone from your device's app store.
1.3 Run the Out-of-Box Demo
NXP’s IoT Toolbox is a versatile mobile application designed to support wireless connectivity demonstrations and testing. It provides an intuitive interface to interact with NXP development platforms.
Get started by installing the IoT Toolbox on your smartphone using the resources shown below:
Open the NXP IoT Toolbox app on your smartphone. Select the wireless universal asynchronous receiver/transmitter (UART) icon. Select the wireless UART LED device. At this point, you should see your device's status as 'Connected' both on the IoT Toolbox app and the serial terminal. Select a number from 0 to 4 to change the LED configuration.
2. Get Software
Watch the video below for directions on how to get the software.
2.1 Install Your Toolchain
NXP offers a toolchain called MCUXpresso for Visual Studio (VS) Code. Please download MCUXpresso for VS Code: v25.09 or newer.

Learn how to install VS Code for your host PC by following the tutorial.
2.2 Jump Start Your Design
The MCUXpresso software development kit (SDK) is complimentary and includes full source code under a permissive open-source license for all hardware abstraction and peripheral driver software. You may install the MCUXpresso SDK directly form the MCUXpresso SDK website . Click on the button below to open this board's SDK builder.
2.3 MCUXpresso Config Tools
The MCUXpresso Config Tool is an integrated suite of configuration tools that guides users in creating new MCUXpresso SDK projects, and also provides pin and clock tools to generate initialization C code for custom board support. It is fully integrated as a part of MCUXpresso integrated development environment (IDE), but also as a separate tool when using a different IDE. Click the Get MCUXpresso Config Tools button below to get the Config Tools installer.

2.4 Programming and Provisioning Tools
The MCUXpresso SEC Tool is a graphical user interface (GUI)-based application provided to simplify the generation and provisioning of bootable executables on NXP microcontroller unit (MCU) devices. We recommend all users to begin with the MCUXpresso Secure Provisioning (SEC) tool for trial run and mass production use. This supports secure programming and device provisioning on NXP's microcontrollers at the production stage.
After downloading the tool, find the user guide under the ‘Help’ tab. Then follow the instructions for your board in the ‘Processor-specific workflow’ chapter.

Note: For advanced users that need a more customizable setup, we also offer a command-line tool that is useful when interfacing with a custom or partner programming tool. The Secure Provisioning SDK (SPSDK) is an open source development kit with its source code released on GitHub and PyPI.
3. Build and Run
While working with one of the demo applications or driver examples, you may be interested to know how you can build and debug them yourself. The Getting Started with MCUXpresso SDK guide provides easy, step-by-step instructions on how to configure, build and debug demos for all toolchains supported by the SDK.
3.1 Updating NBU for Wireless Examples
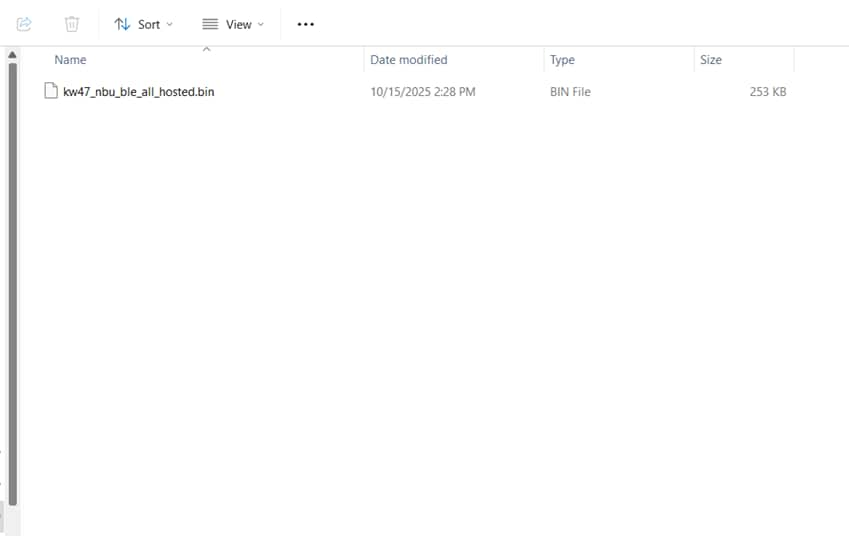
Be aware that it is necessary to work with the matching narrow band unit (NBU) image for the SDK version of the application you are working with. This means that when you download your SDK, prior to loading any wireless SDK example, update your NBU image with the provided binaries in the following folder of the SDK:
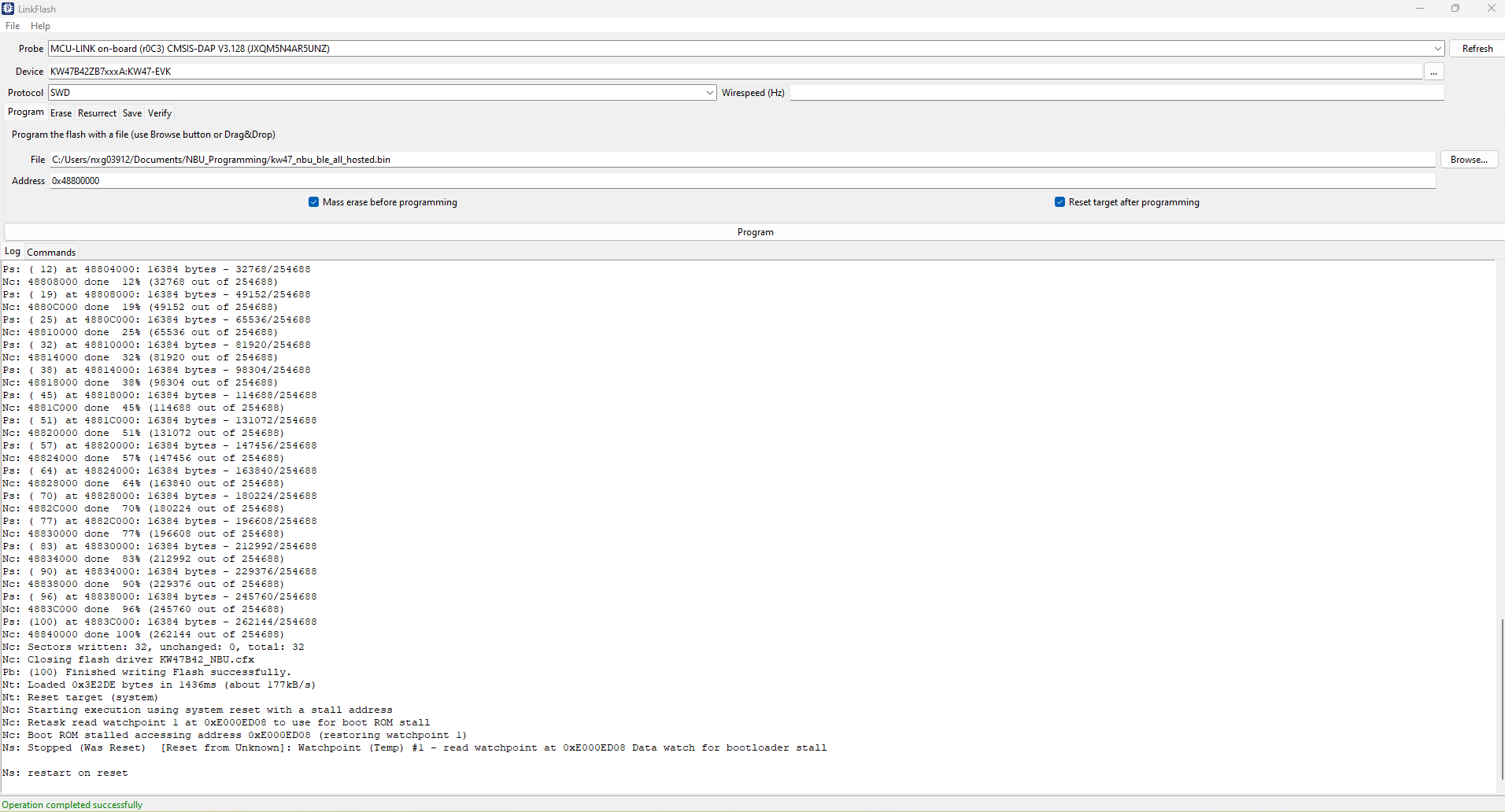
../middleware/wireless/ble-controller/binTo update the NBU, you may use the LinkFlash tool as follow:
-
Open the path to LinkFlash tool. Usually, this path would be:
C:\nxp\LinkServer_xx.x.xx - Select
KW47B42ZB7xxxA:KW47-EVKas device, serial wire debug (SWD) as protocol and 0x48800000 as address. Check the 'Mass erase before programming' checkbox. - Select '
kw47_nbu_ble_all_hosted.bin' as image file. Press the 'Program' button and wait for the flash operation to be completed.
3.2 Build and Flash Application using MCUXpresso for VS Code IDE
The following steps will guide you through the wireless_uart demo application using MCUXpresso for VS Code IDE for
the Arm® Cortex®-M33 application. The MCUXpresso for VS Code IDE installation and the SDK for the KW47 can be found at the
section Get Software of this Getting
Started guide.
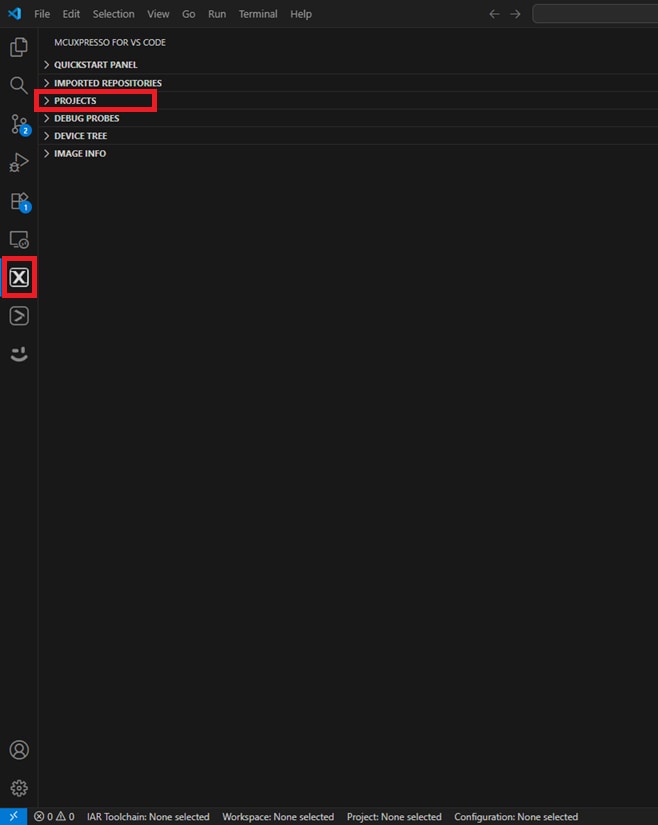
- Click the MCUXpresso for VS Code icon on the left side of VS Code to open the Activity Bar. Then, click the "Projects" tab.
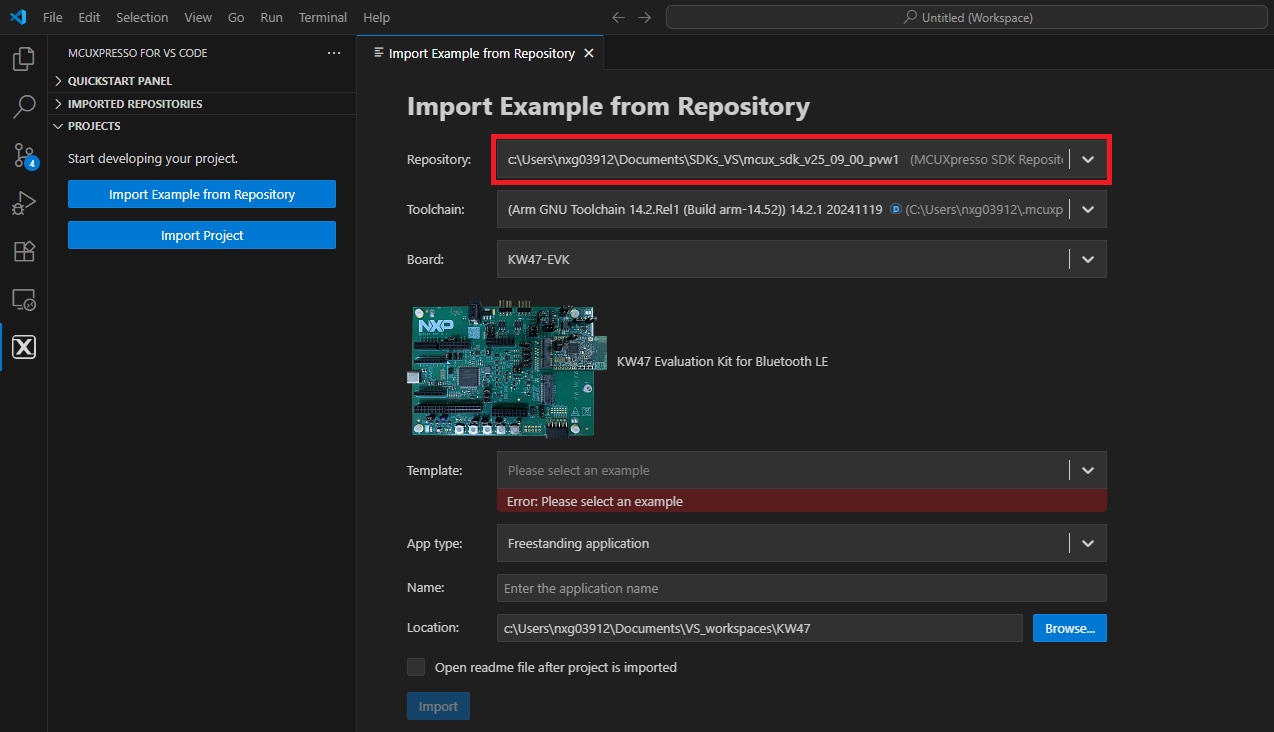
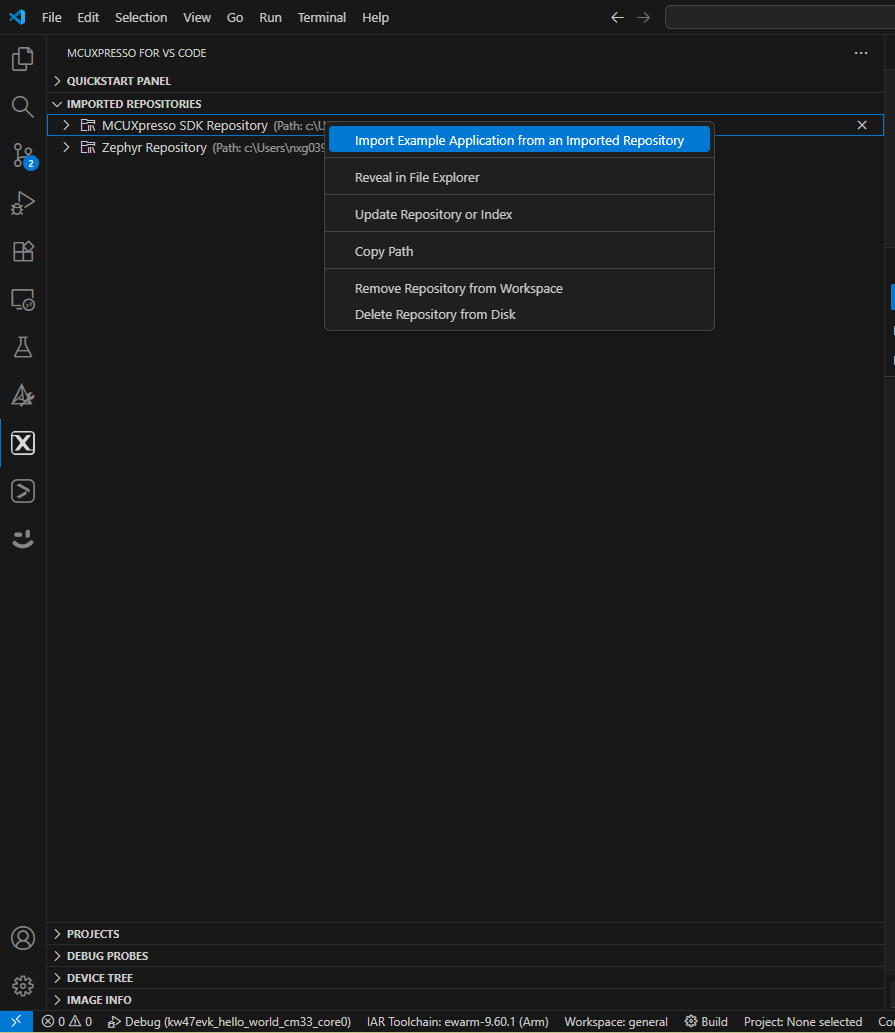
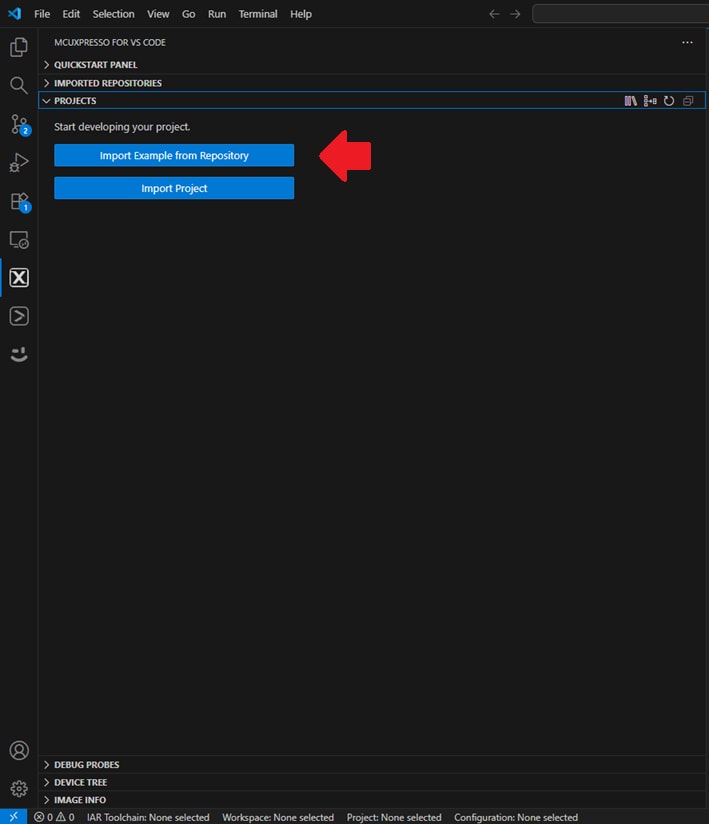
- Click the Import example from Repository option
- Click the Repository dropdown arrow to choose your previously downloaded KW47-EVK SDK
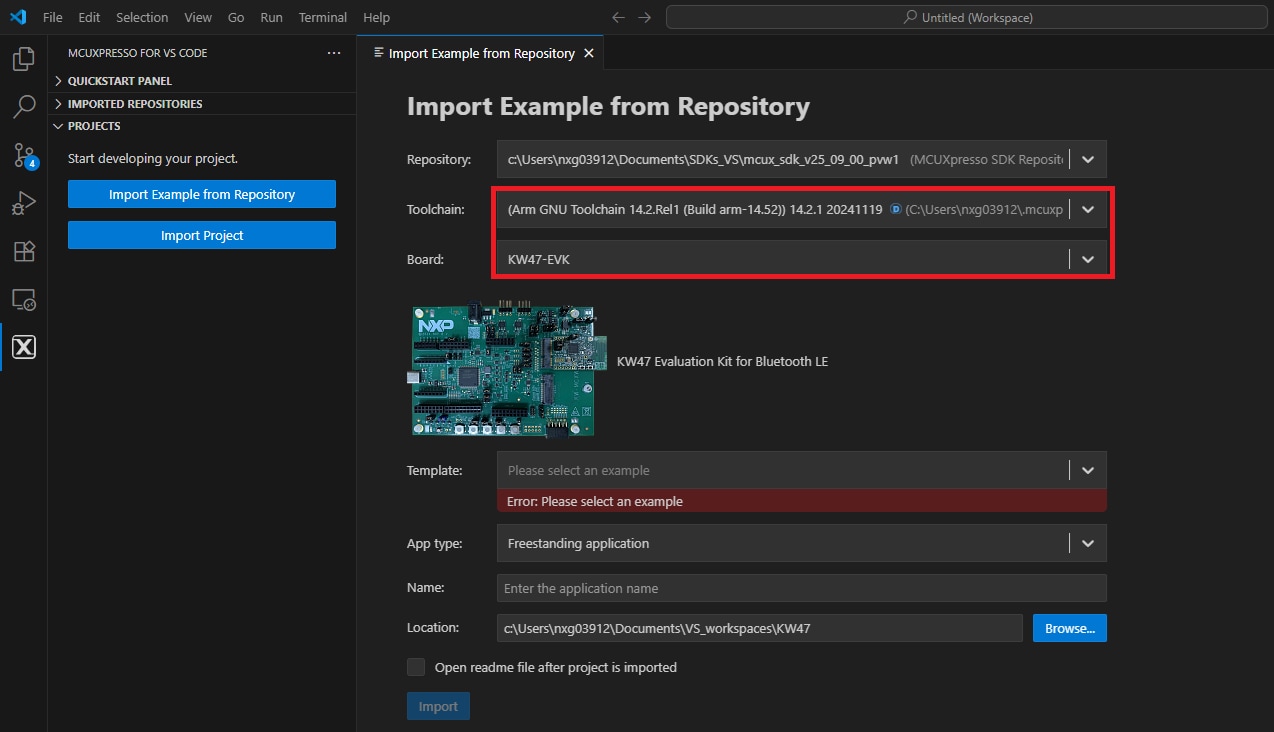
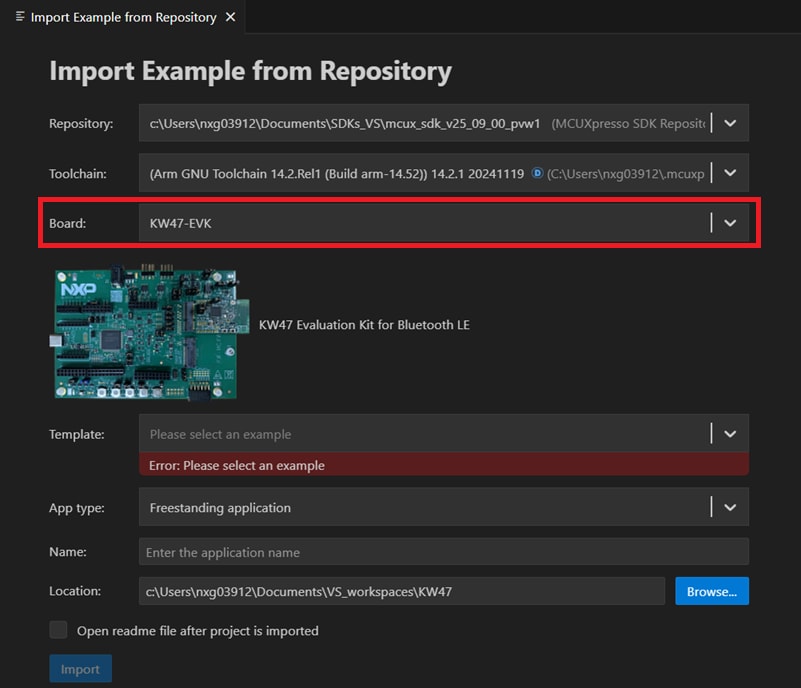
- Click the Toolchain dropdown arrow to select the latest version of the Arm GNU Toolchain. Then, from the Board dropdown list, choose the KW47-EVK option to select a template application compatible with that board
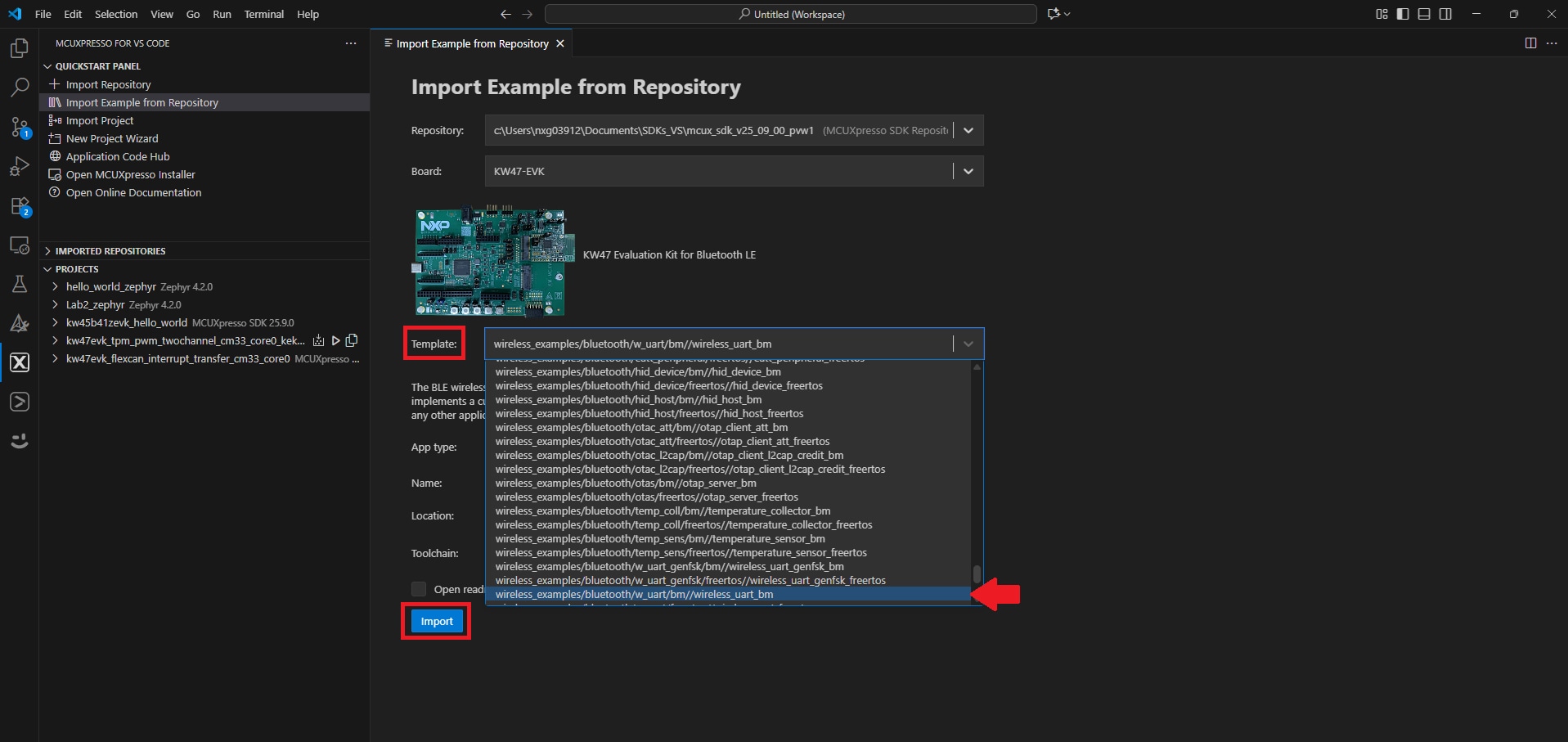
- Click the Template dropdown arrow and select . Then, click the Import button
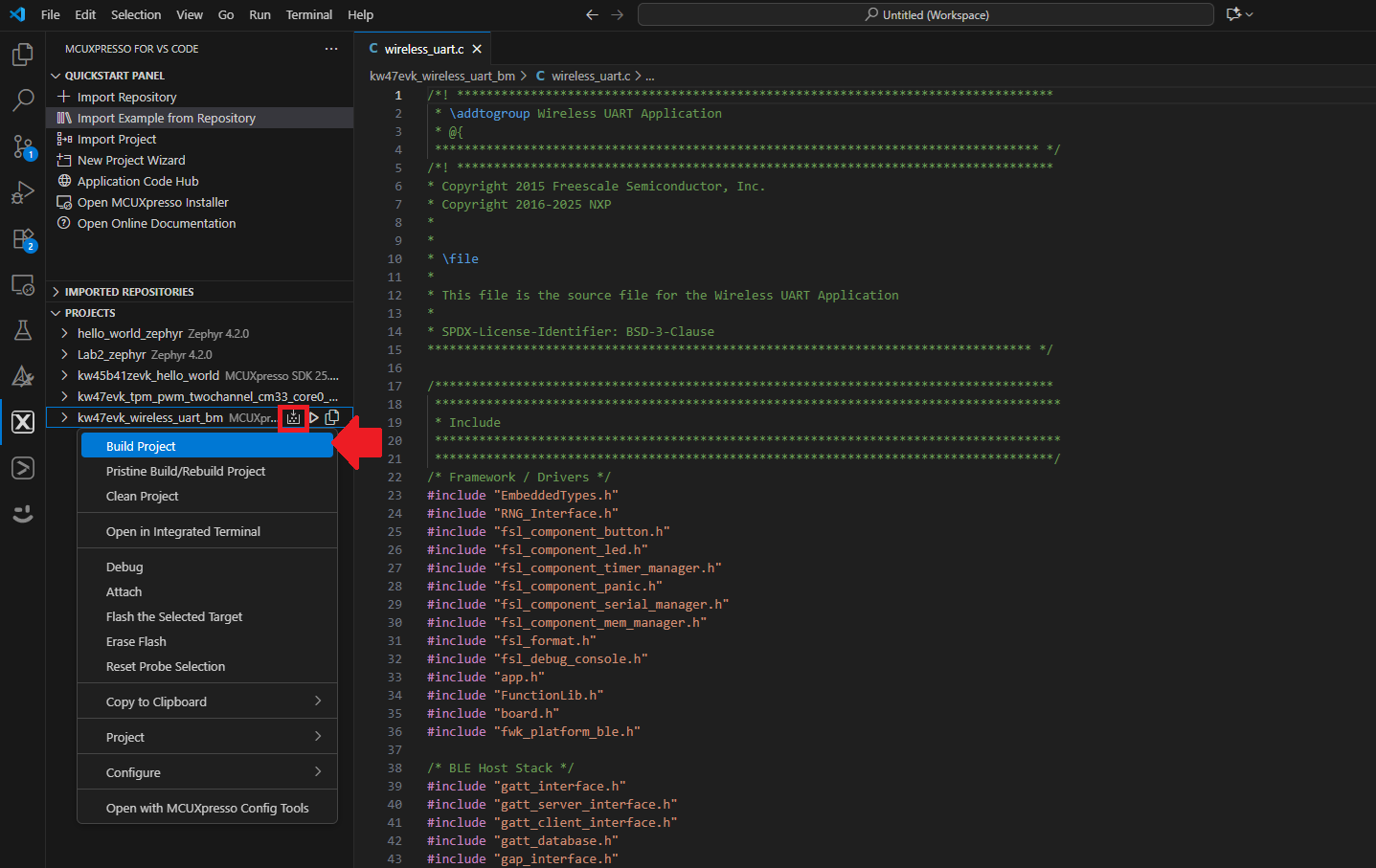
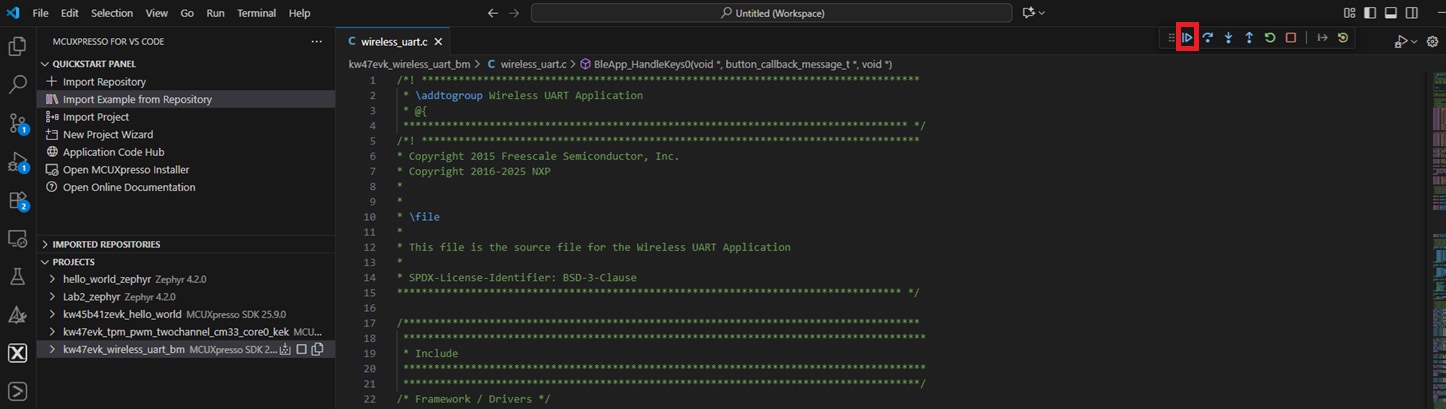
wireless_examples/bluetooth/w_uart/bm//wireless_uart_bm - Expand the Projects tab located under the Activity Bar. Right-click your previously created project and select Build Project. You can also click the Build Project icon next to the project's name
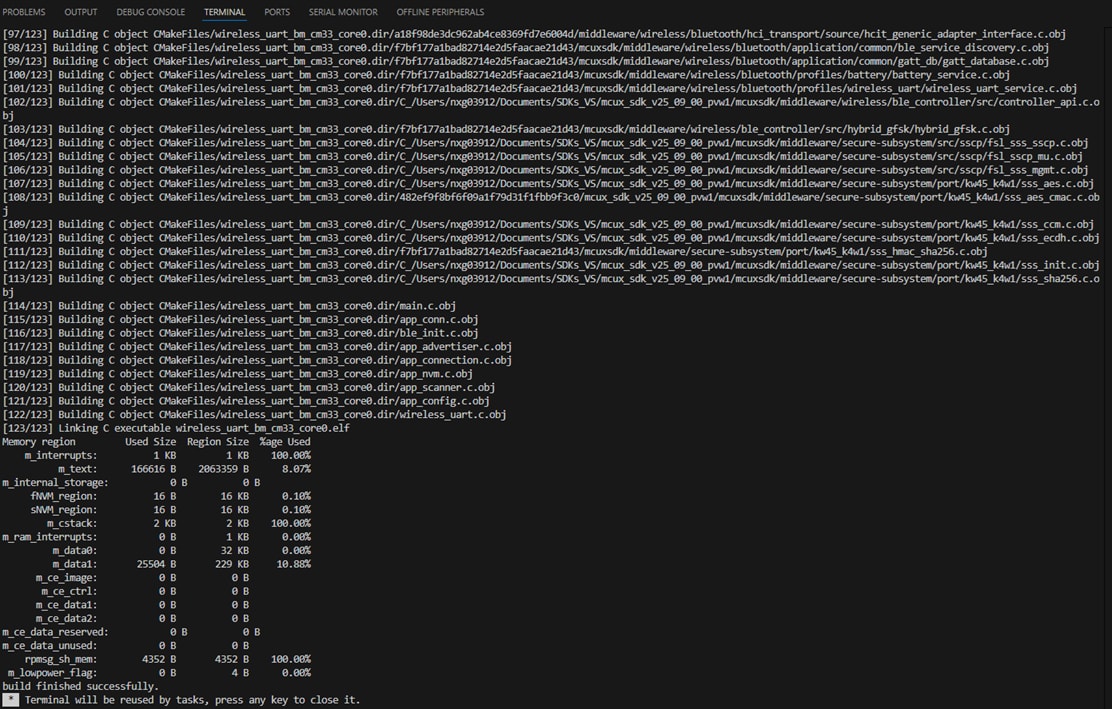
- The project should build without any errors or warnings in the console
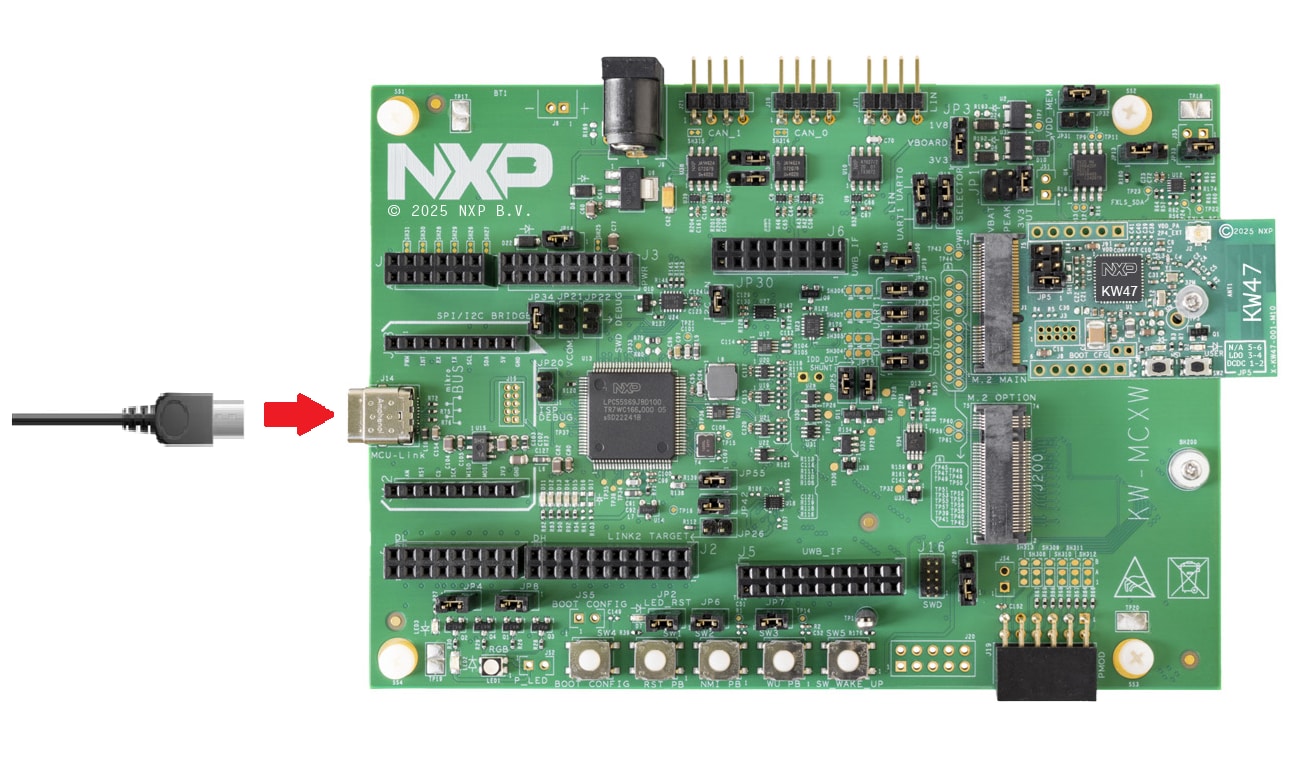
- Connect the board to your computer with the micro USB to
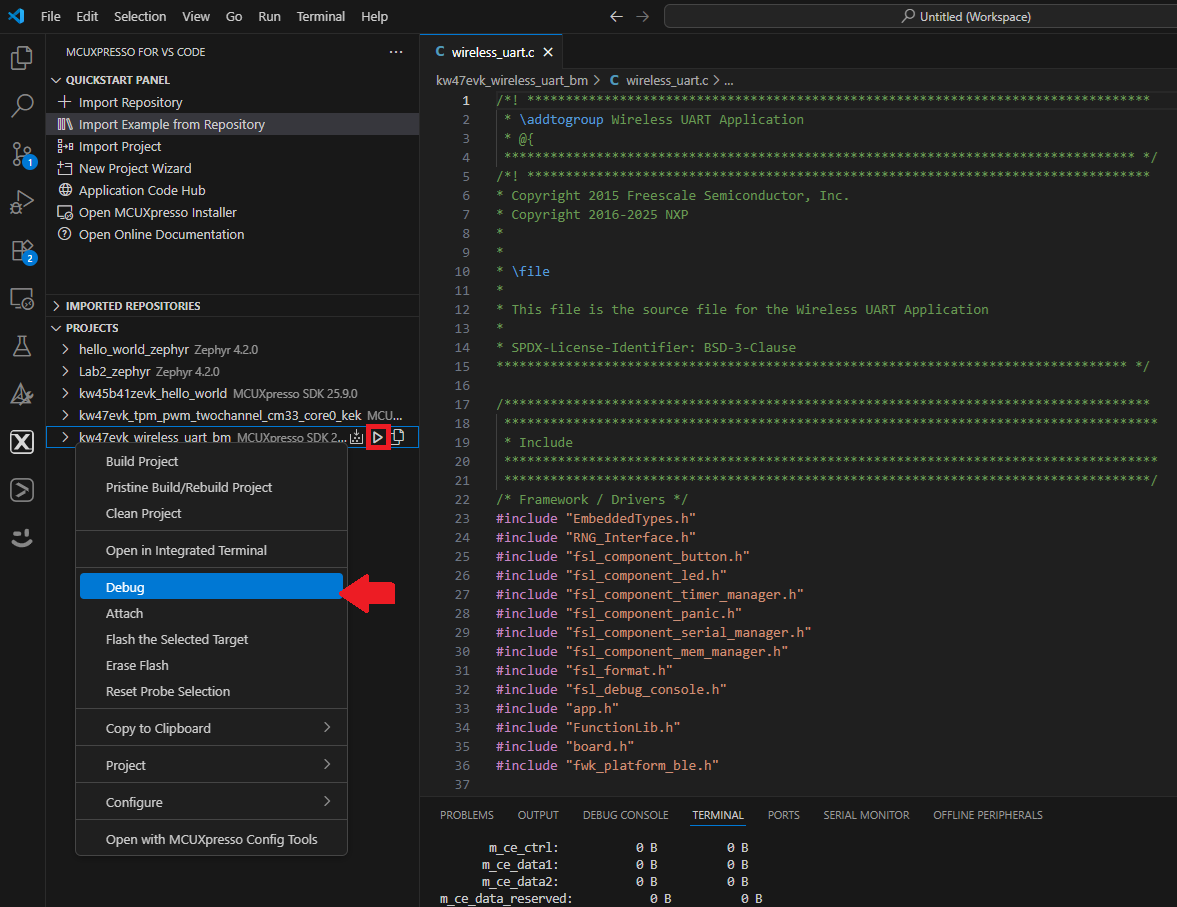
J14‘MCU-LINK’ port - Right-click your previously created project and select Debug. You can also click the Debug icon next to the project's name. This will download the application to your board
- VS Code supports a native serial terminal that you can use to view your application's output. Click the Serial
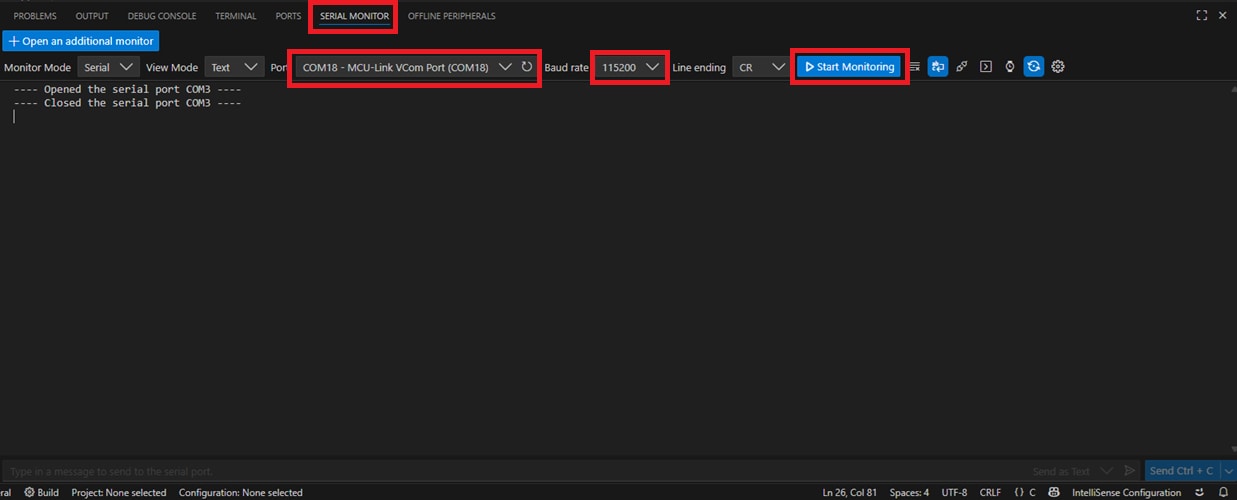
Monitor option in the Panel. Then, select
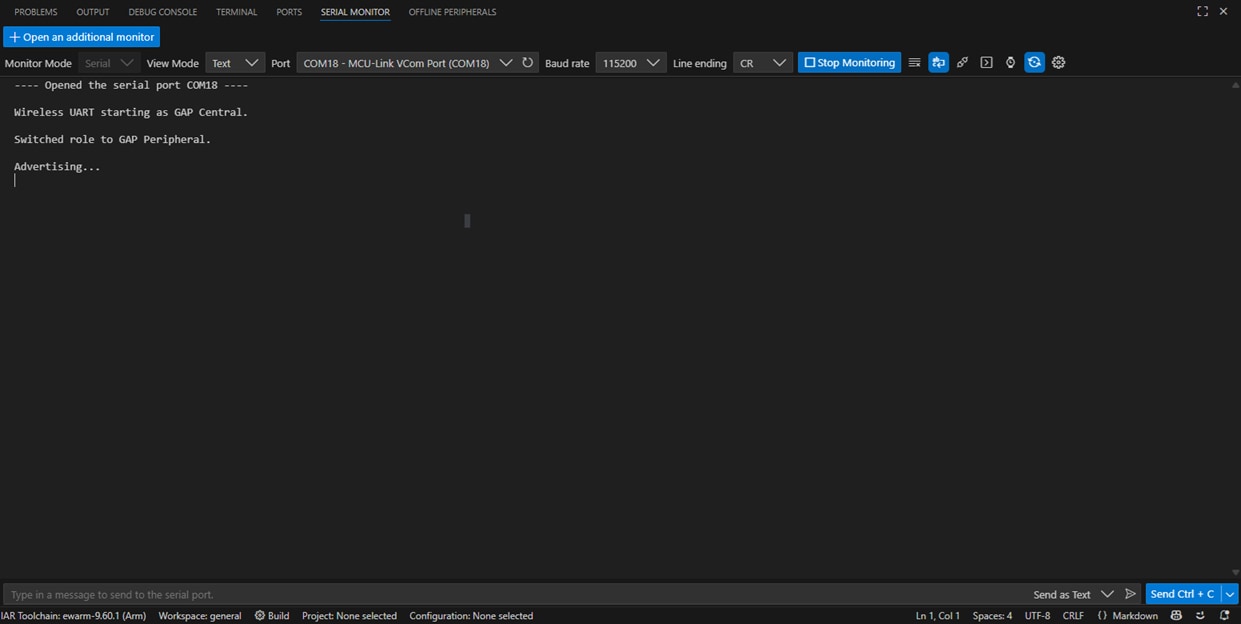
COMx - MCU-Link VCom Portas the Port, and set the Baud rate to 115200. Finally, click Start Monitoring - Run the application by clicking the Continue icon. Press the View the output in the Serial Monitor. Press
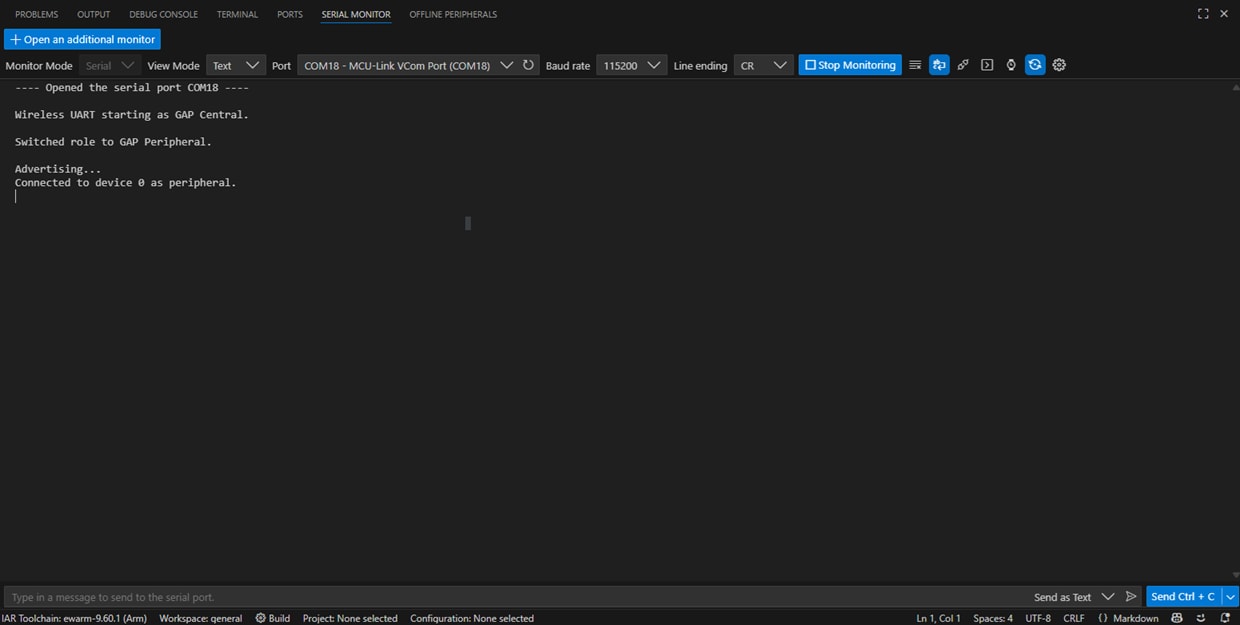
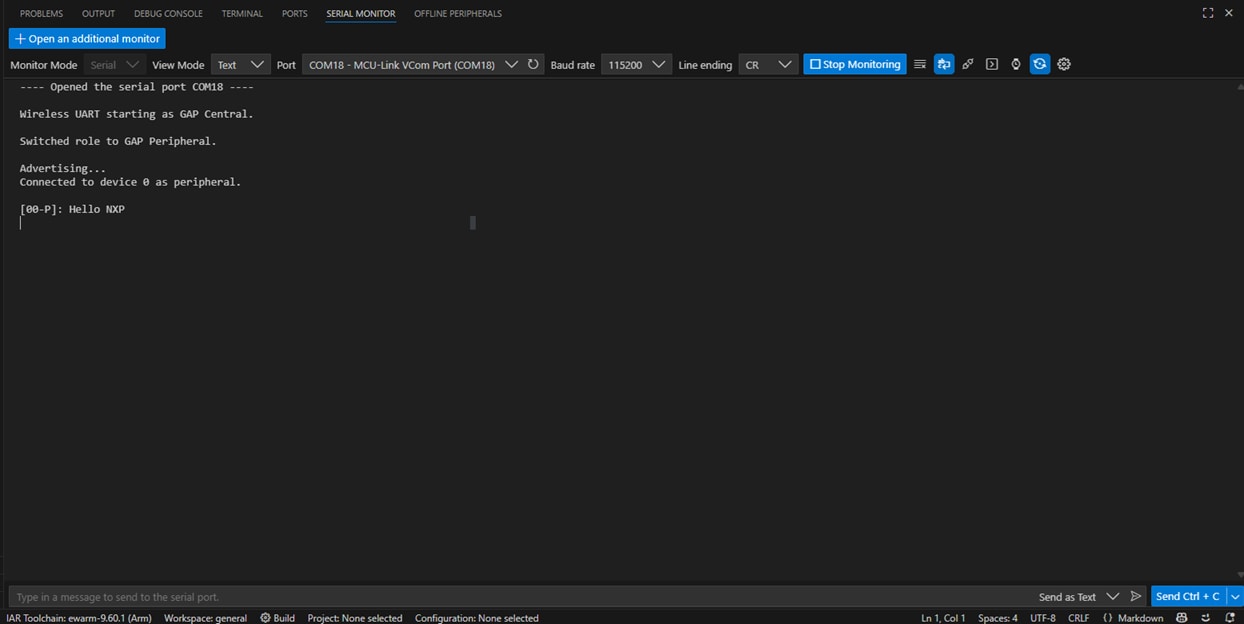
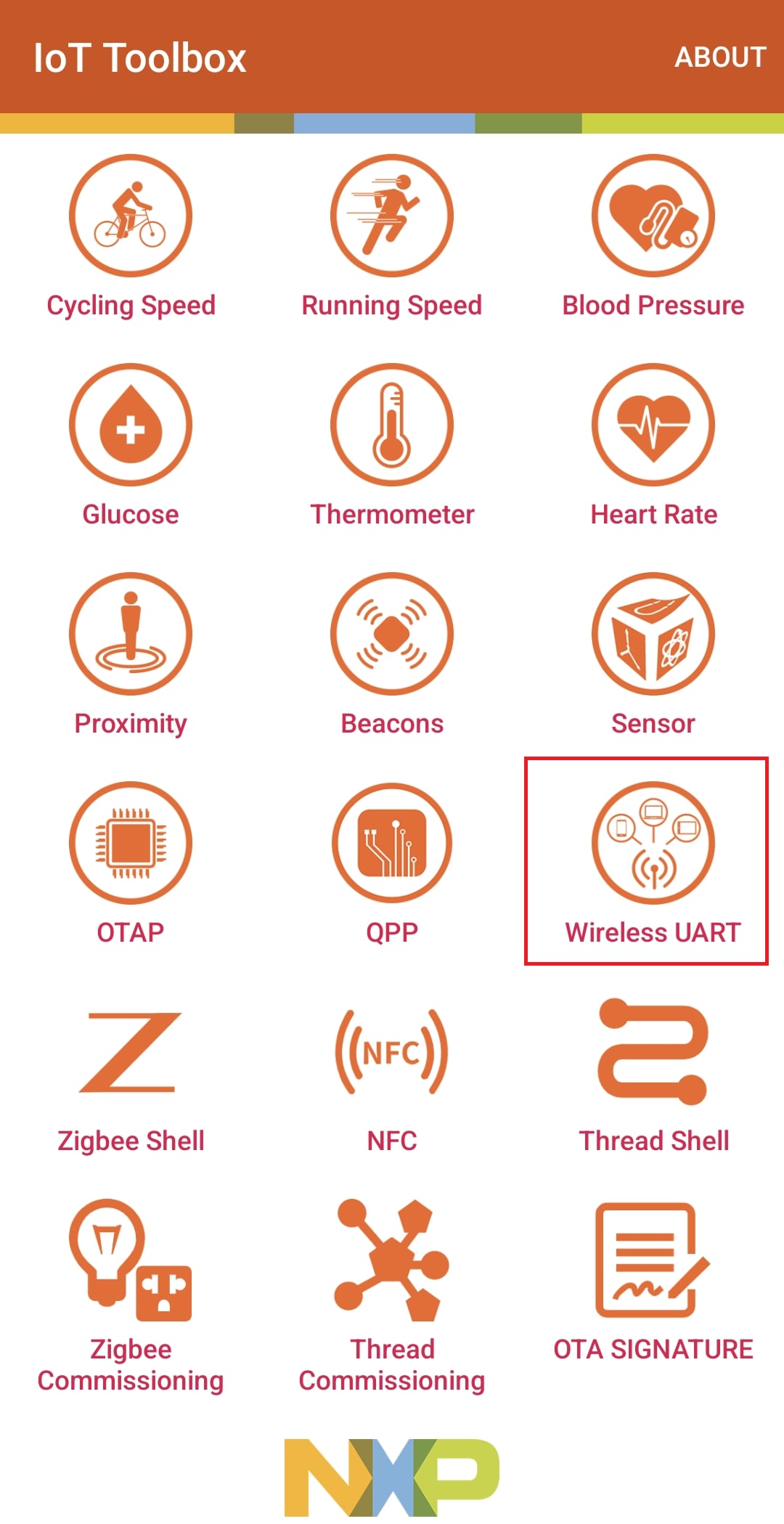
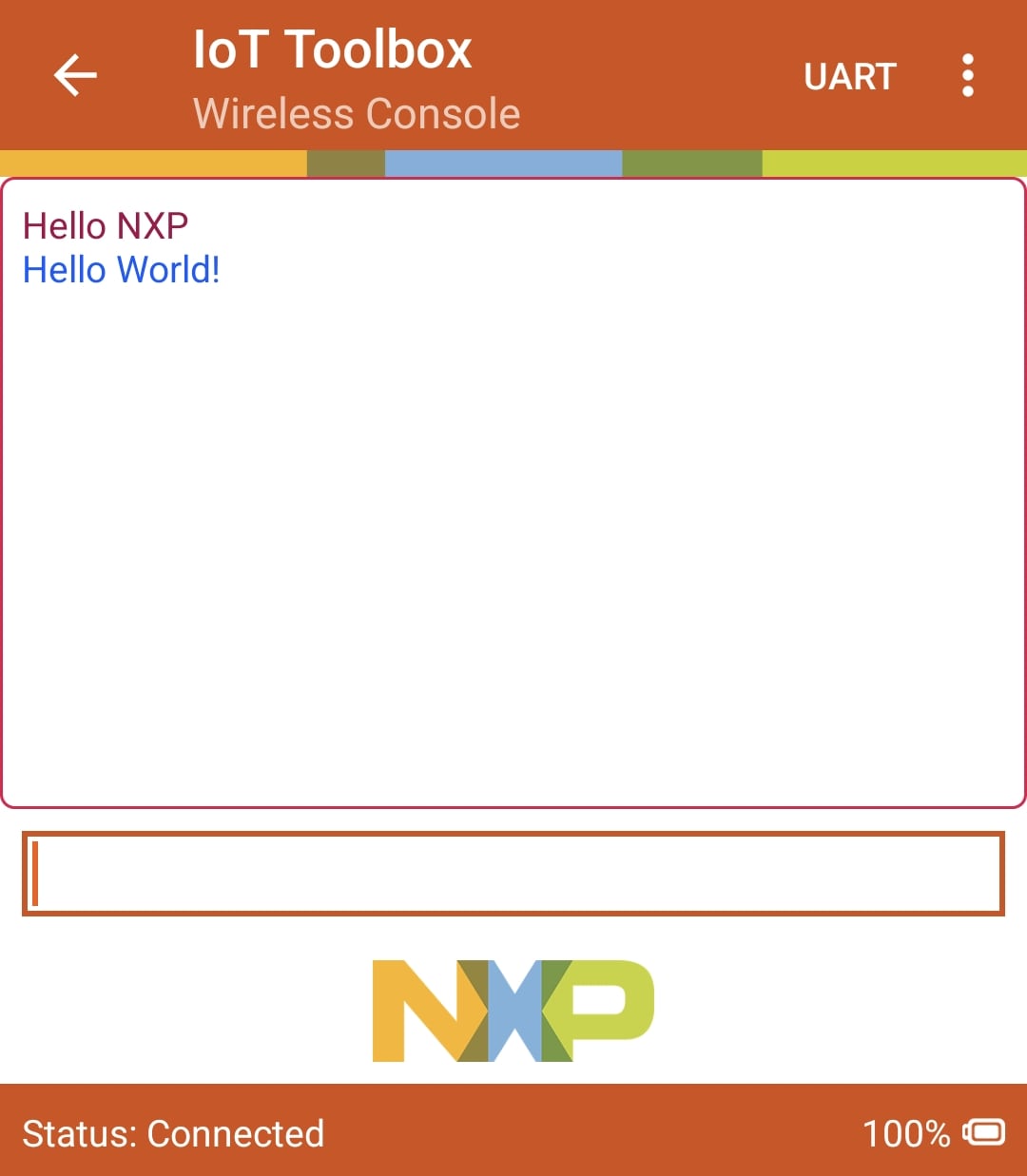
SW3button to switch the BLE role to peripheral. Then pressSW2to start BLE Advertising. You should see the messages printed on the terminal - Open your NXP's IoT Toolbox app in your smartphone. Select the wireless UART icon. Select the wireless UART commen device. At this point, you should see your device's status as 'Connected' both on the IoT Toolbox app and the serial terminal
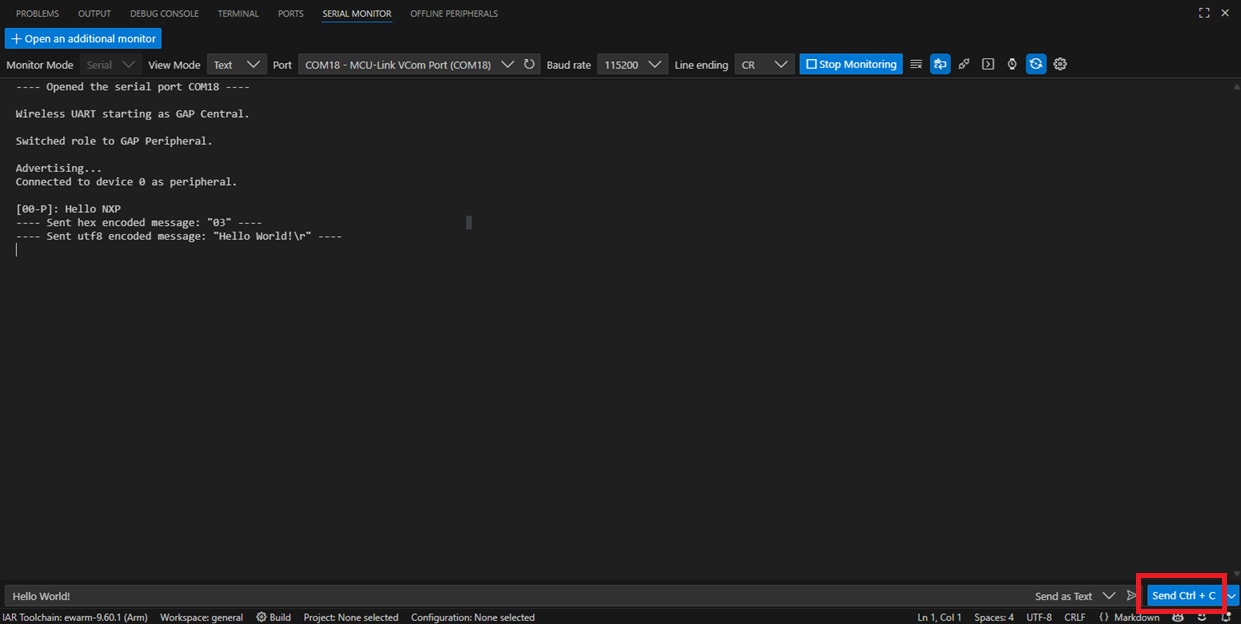
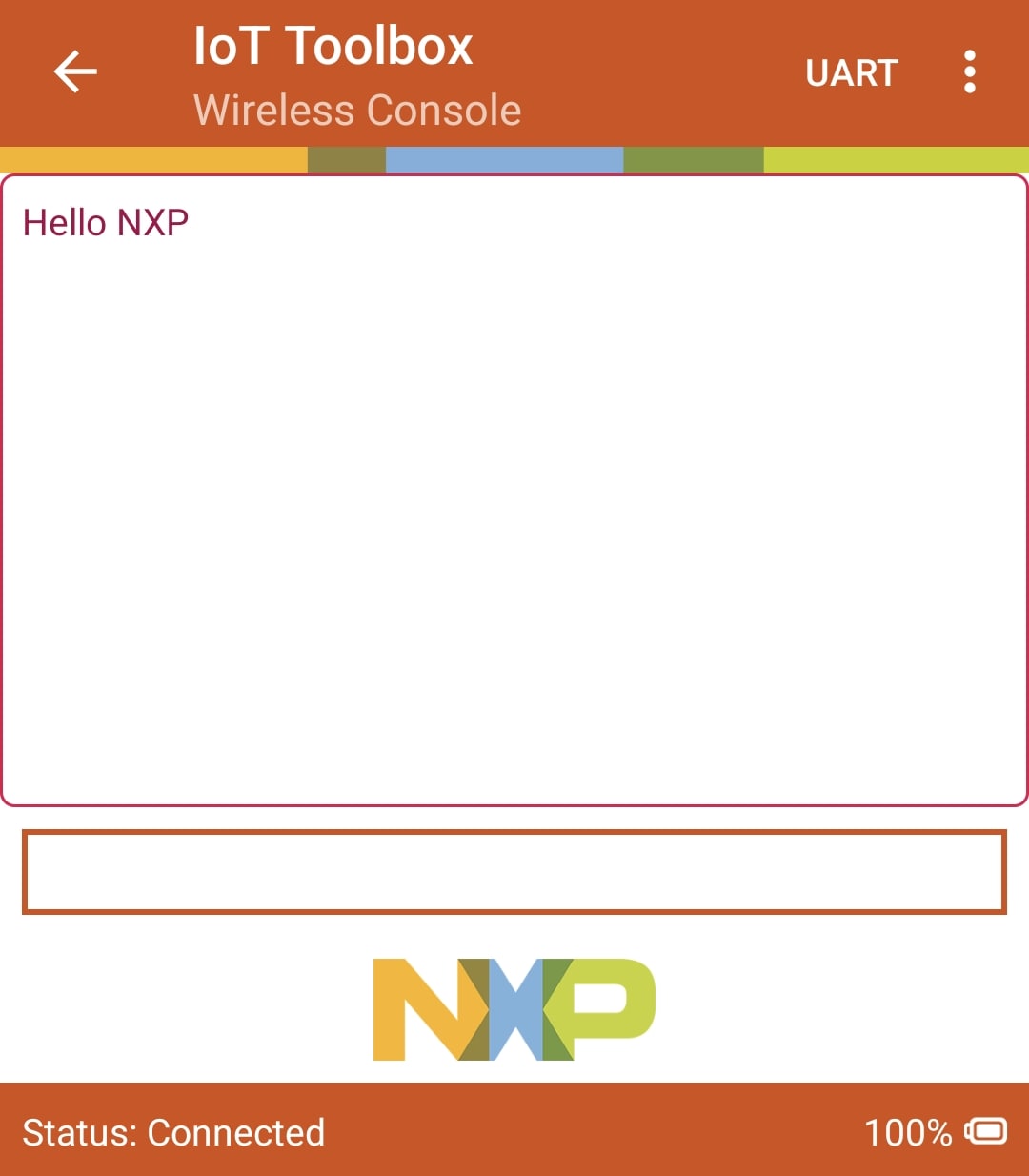
- Type and send any message on the NXP's IoT Toolbox app. See it displayed on the serial terminal
- Type and send any message on the serial terminal. See it displayed on the NXP's IoT Toolbox app

3.3 Build and Flash Application with Alternative Toolchains
MCUXpresso for VS Code provides an optimized embedded developer experience for code editing and development. Learn how to build and flash an application with VS Code.
Using a different toolchain?
Demos are also available for IAR and KEIL.
4. Create
4.1 Clone an Example Project from MCUXpresso for VS Code IDE
The following steps will guide you through the manipulation of the general-purpose outputs (GPOs). The example sets up a timer PWM module (TPM) to generate a pulse width modulator (PWM) signal and change the RGB LED brightness.
- Expand the "IMPORTED REPOSITORIES" tab, then right-click your previously downloaded KW47-EVK SDK. Next, select "Import Example Application from an imported Repository"
- Click the "Board" dropdown list, then choose the KW47-EVK option to select the template application compatible with that "Board"
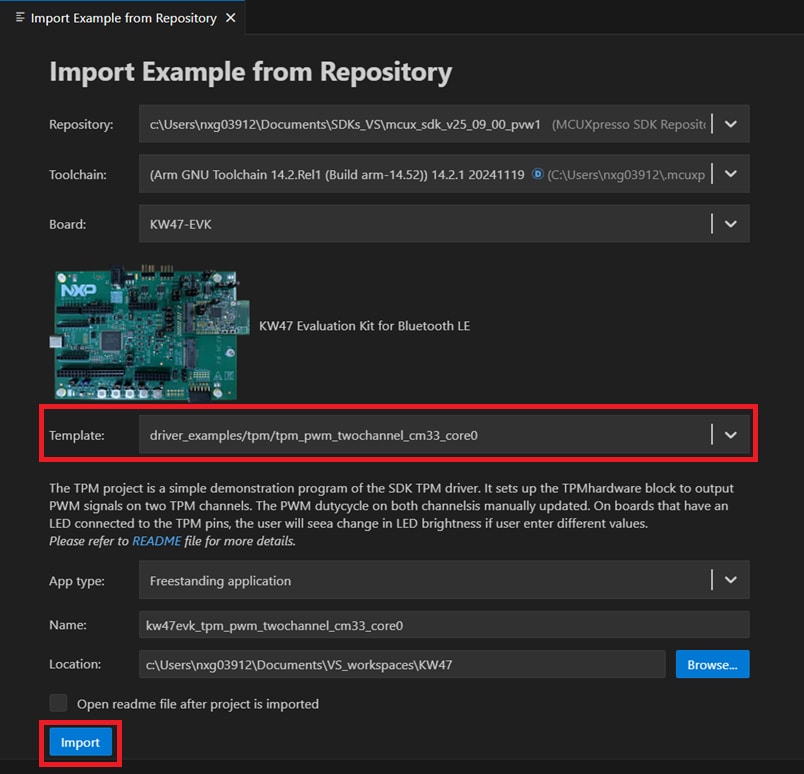
- Click the Template dropdown arrow and select: Then, click the "Import" button.
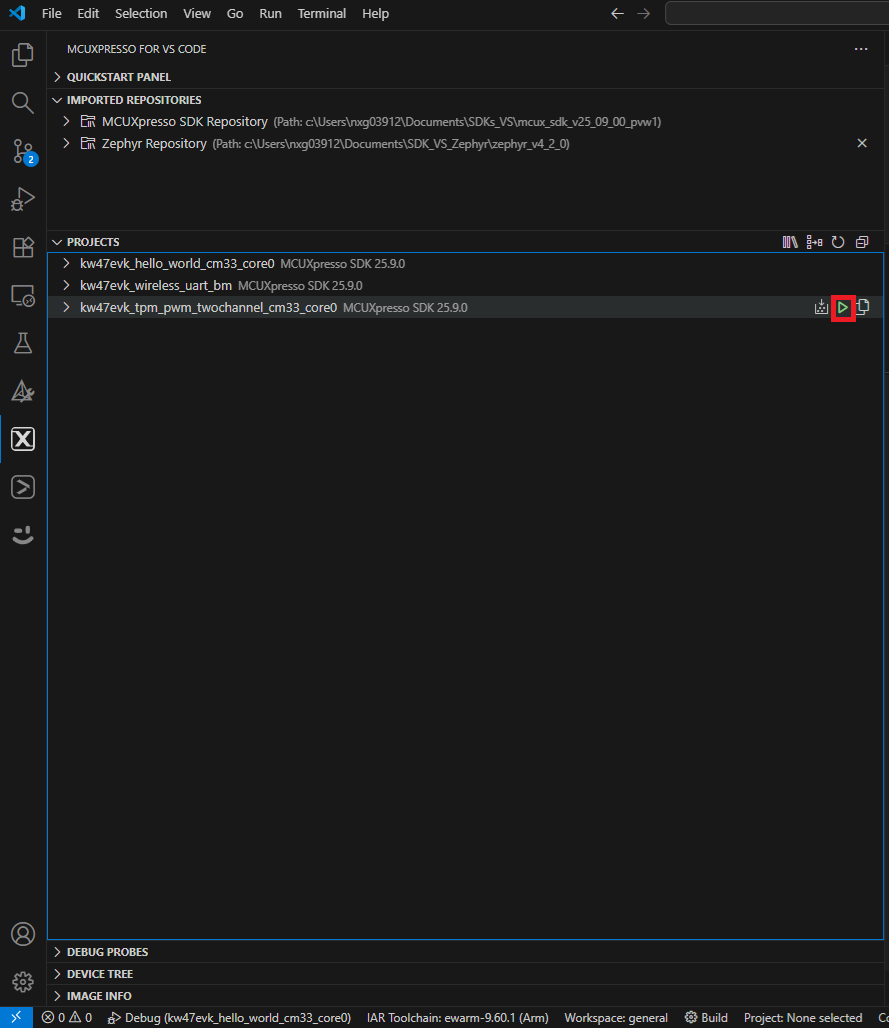
driver_examples/tpm/tpm_pwm_twochannel_cm33_core0 - Right-click your previously created project and select "Debug". You can also click the Debug icon next to the project's name. This will download the application to your board.
- VS Code includes a native serial terminal that you can use to view your application's output. Click the Serial
Monitor option in the Panel. Then, select
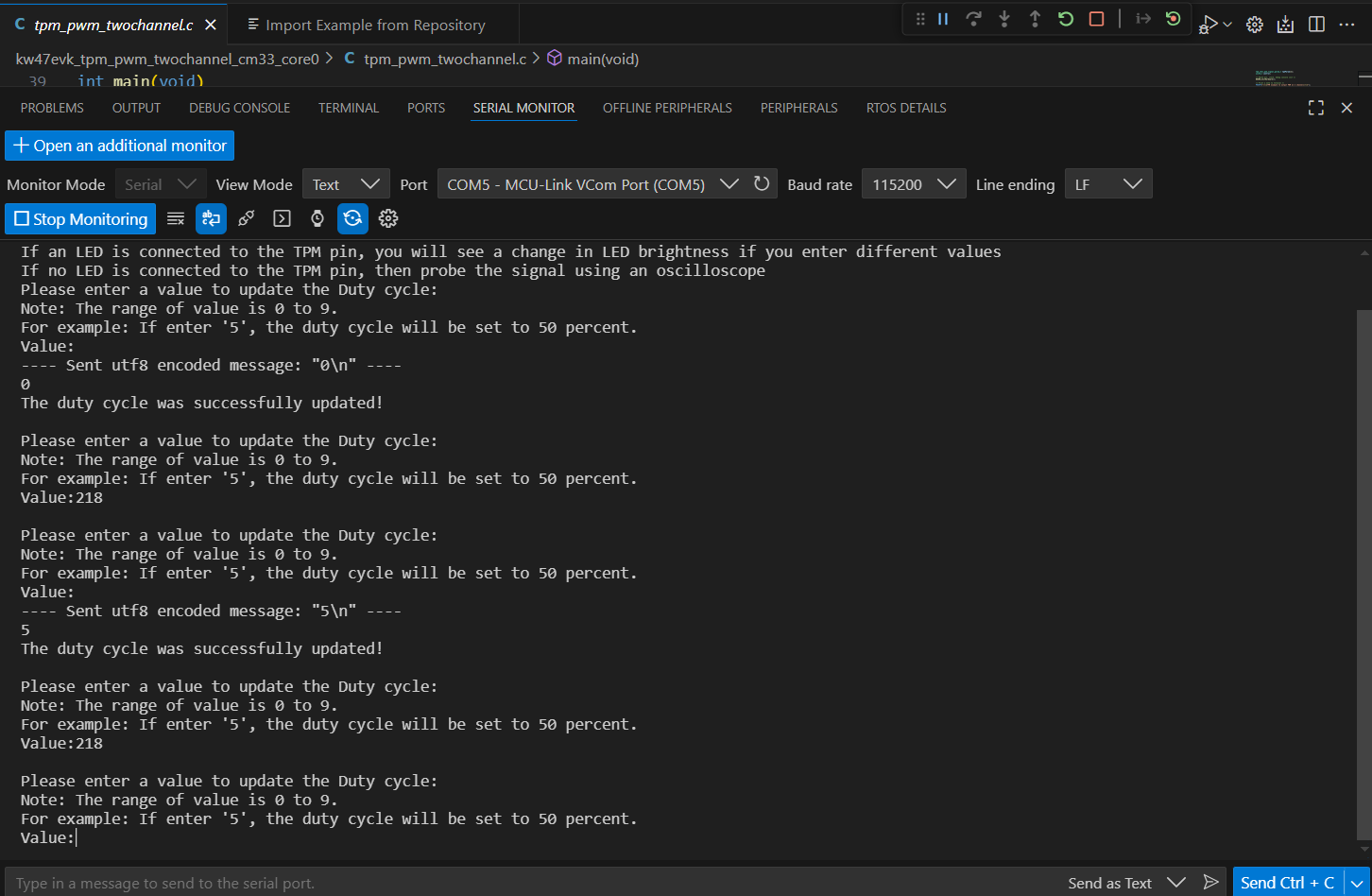
COMx - MCU-Link VCom Portas the Port, and set the Baud rate to 115200. Finally, click Start Monitoring - Run the application by clicking the Continue icon. View the output in the Serial Monitor. The application will prompt you to enter a number between 0 and 9. This number adjusts the RGB LED brightness by modifying its duty cycle
4.2 Clone an Example Project using MCUXpresso Config Tool for 3rd Party IDE
The following steps will guide you through the manipulation of the general-purpose outputs. The example sets up a TPM to generate a PWM signal and change the RGB LED brightness.
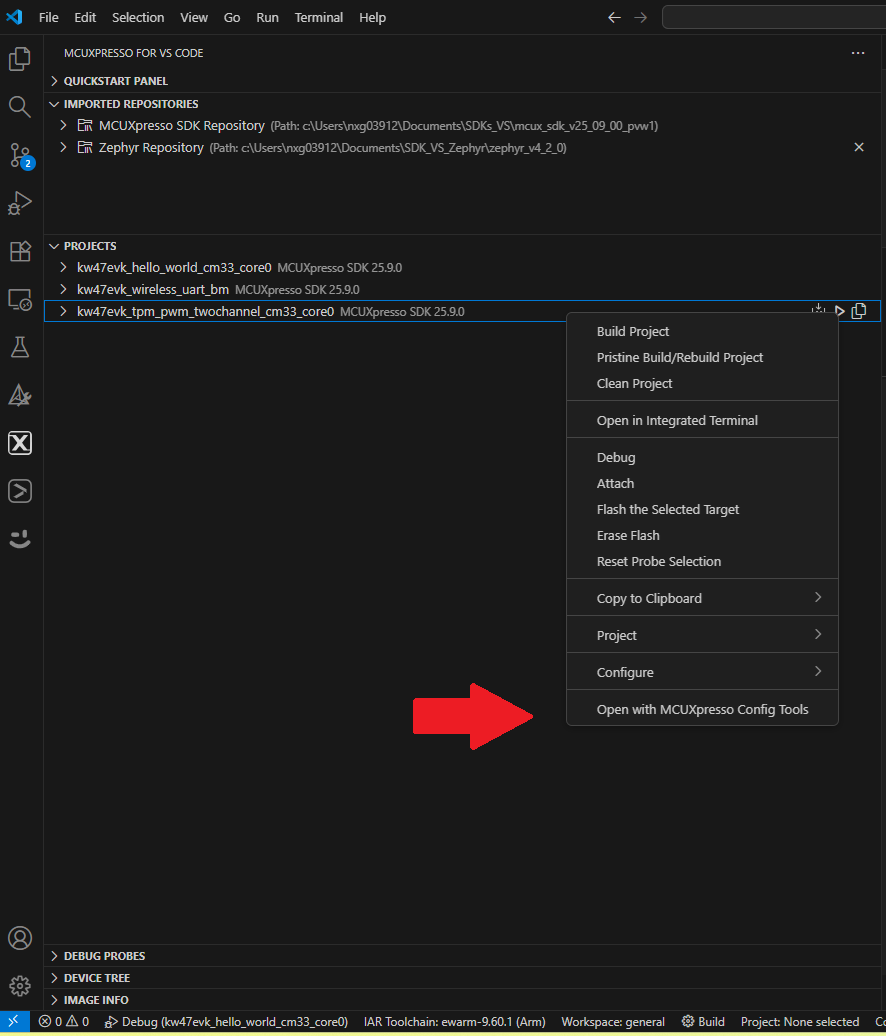
- Expand the Projects tab located under the Activity Bar. Right-click your previously created project and select "Open with MCUXpresso Config Tools"
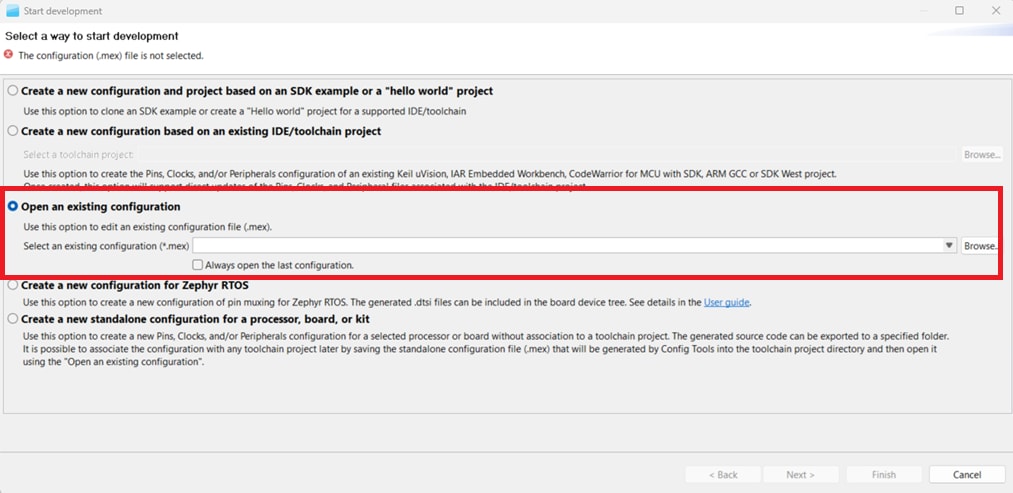
- When the wizard appears, select the “Open an existing configuration” button and click on "Next". If your
imported project does not contain a configuration
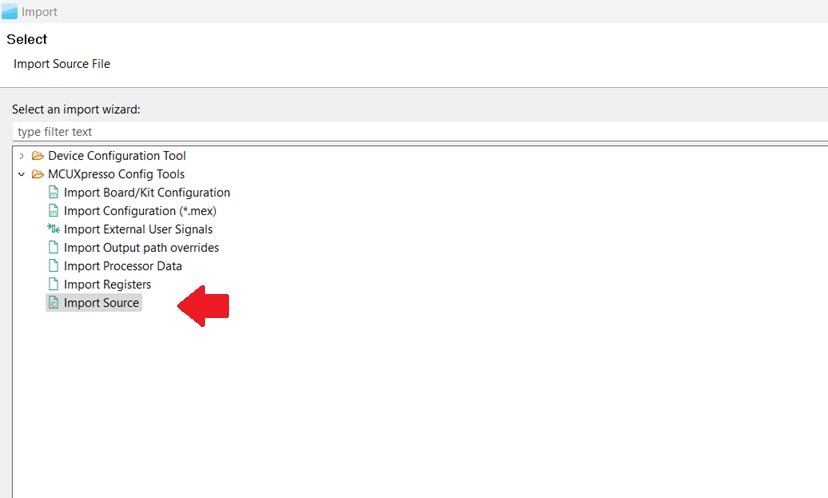
.mexfile, just click "Cancel". - On the next screen, select the "Import Source" option from the Import wizard. After this, click on the "Next" button.
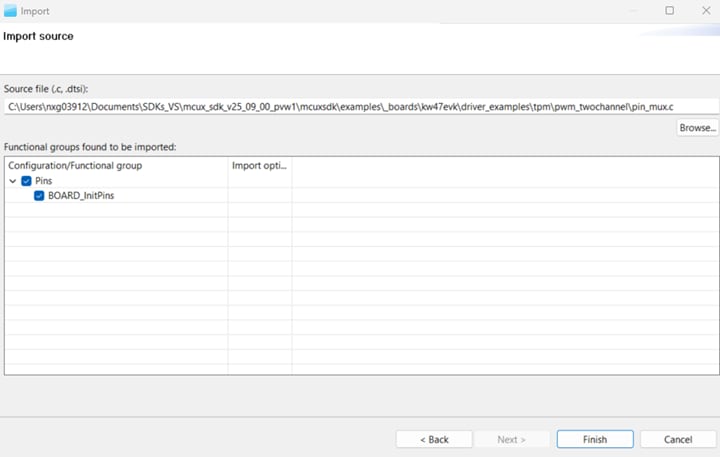
- On the next screen, click on the "Browse" option. After this, search for the pin_mux.c source file to import. This
file can be found in the following path: Click on the "Finish" button.
\mcuxsdk\examples\_boards\kw47evk\driver_examples\tpm\pwm_twochannel - After the source file is imported, the MCUXpresso Config Tools interface should display your project's pin configuration.
4.3 Use the Pins Tools to Modify the LED Routed Pin
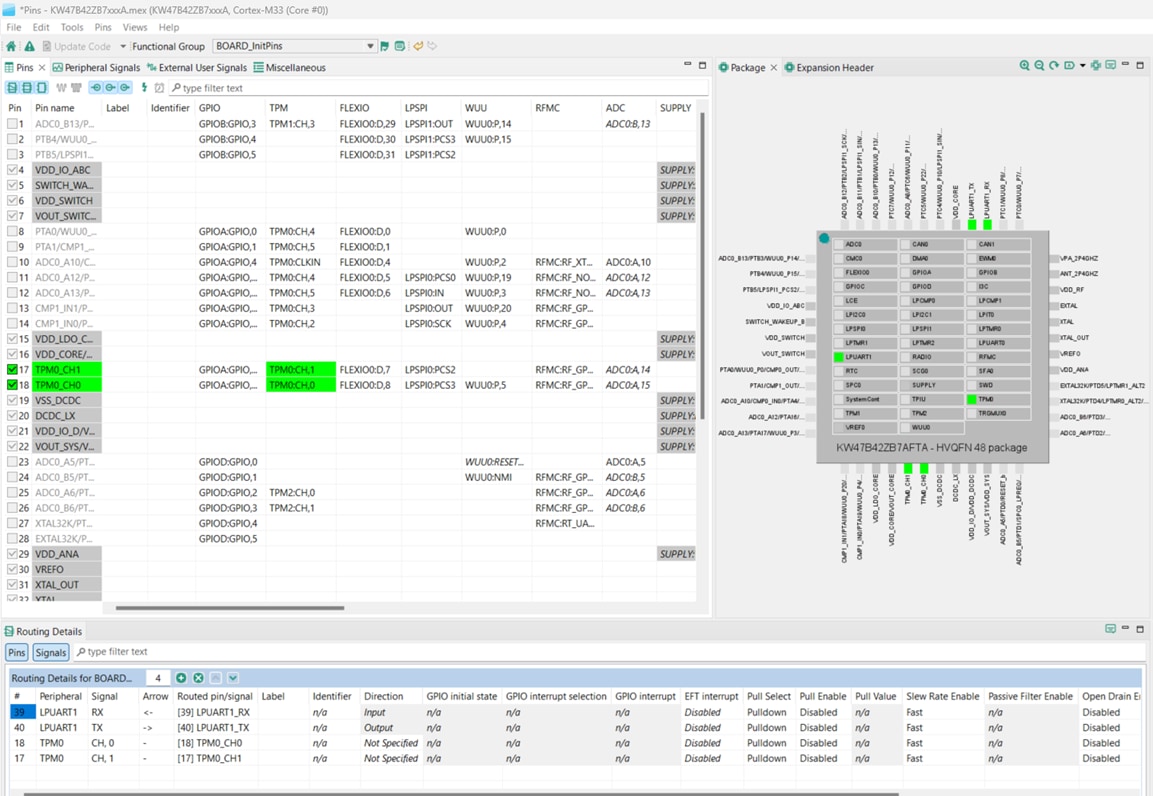
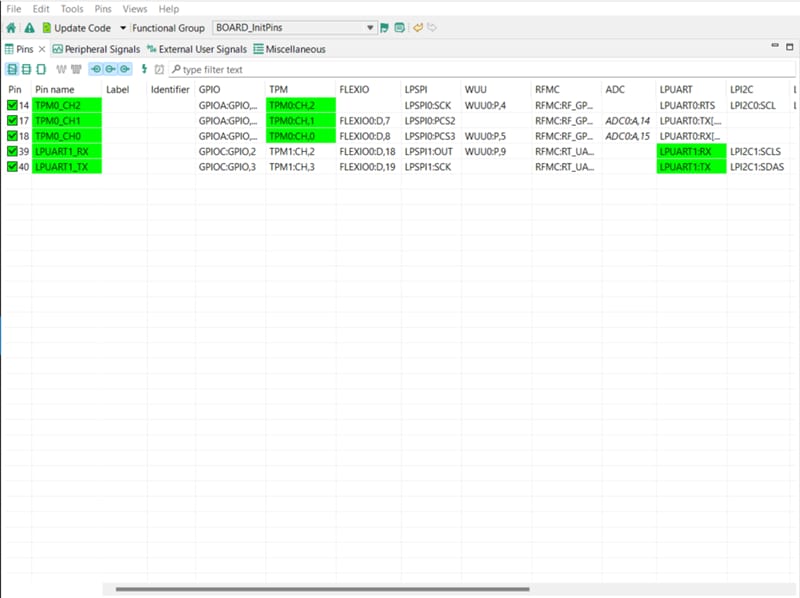
We’ll use MCUXpresso Config tools for the rest of the instructions. In the Pins view deselect “Show dedicated pins” and “Show no routed pins” checkboxes so that only routed pins are shown. Routed pins have a check in a green box next to the pin name.
- The functions selected for each routed pin are highlighted in green.
- In the current configuration,
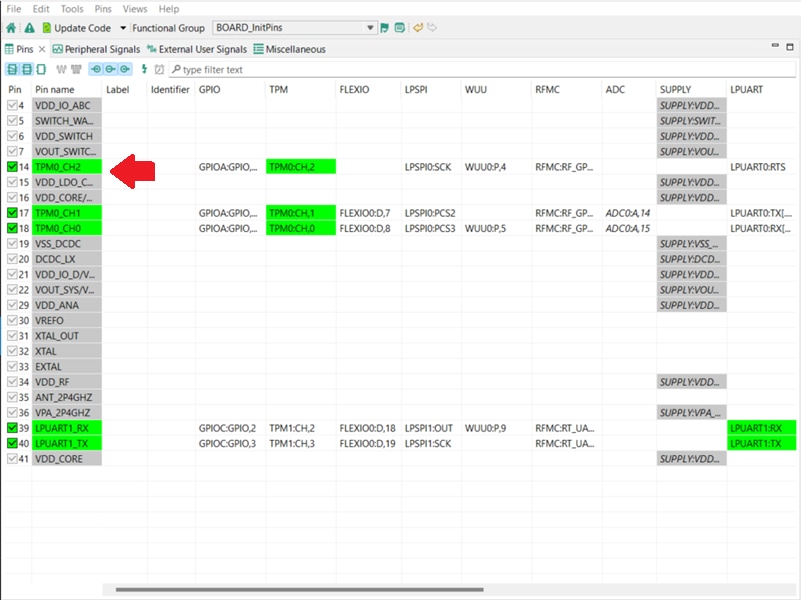
PTA20andPTA21are routed as the outputs of the "TPM". Here you will add the pin configuration to enable the GREEN LED. - Select “Show no routed pins” to see the other options. To enable the GREEN LED, search for
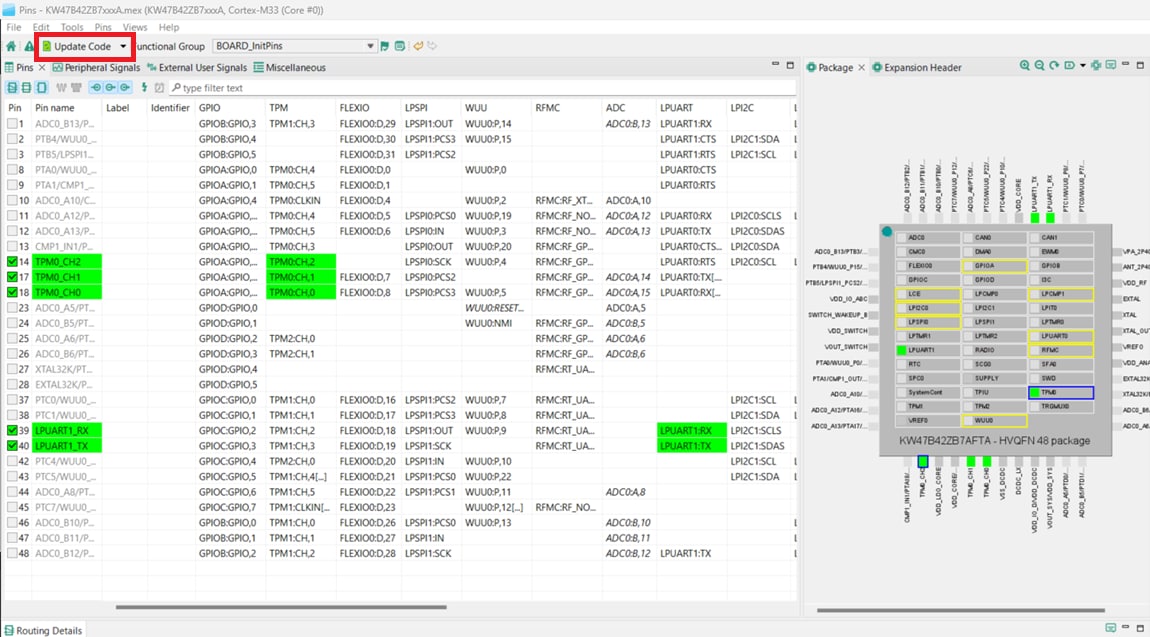
PTA19and selectTPM0_CH2, under the "TPM" column. - Now it’s time to implement these changes into the project by exporting the new updated
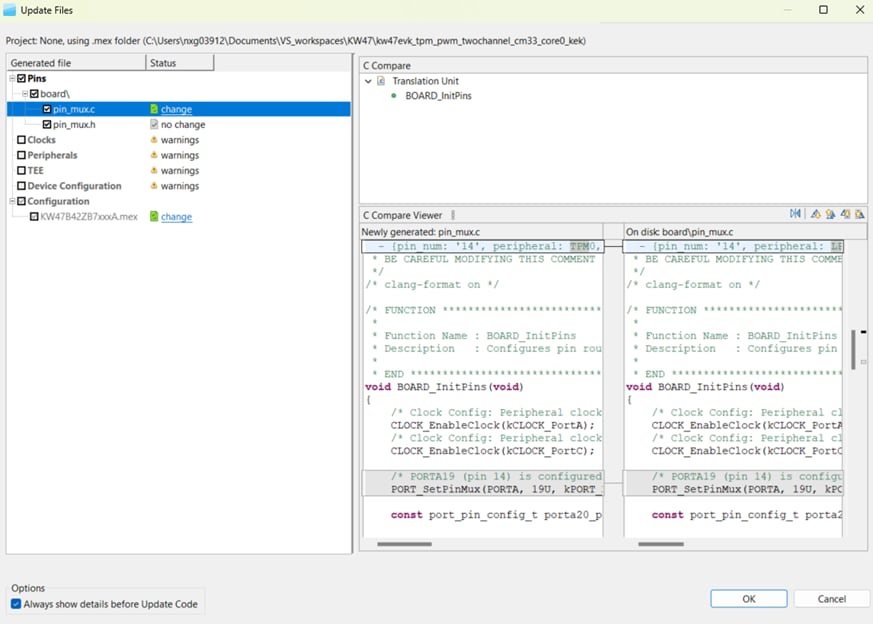
pin_mux.candpin_mux.hfiles that are generated by the Pins tool. If the configuration file (.mexfile) is not saved the disk, save it by using the File menu option. Next, click on "Update Project" in the menu bar - The screen that pops up will show the files that are changing and you can click on “diff” to see the difference between the current file and the new file generated by the Pins tool. Click “OK” to overwrite the new files in your project.
- After this, Config tools should have generated the corresponding pin configuration source code. Source code is
generated on the board folder; located on the same directory as your configuration file (
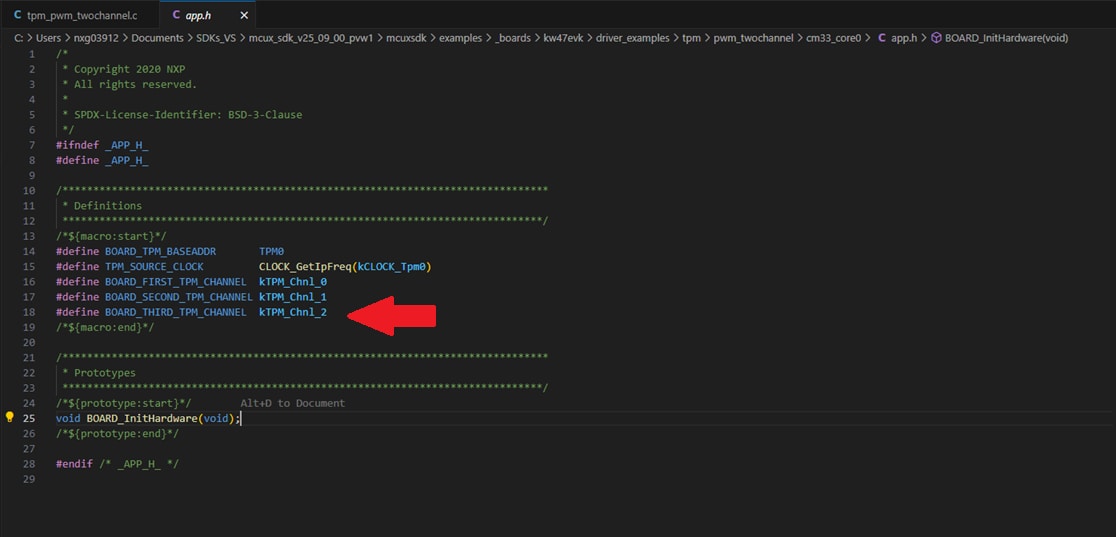
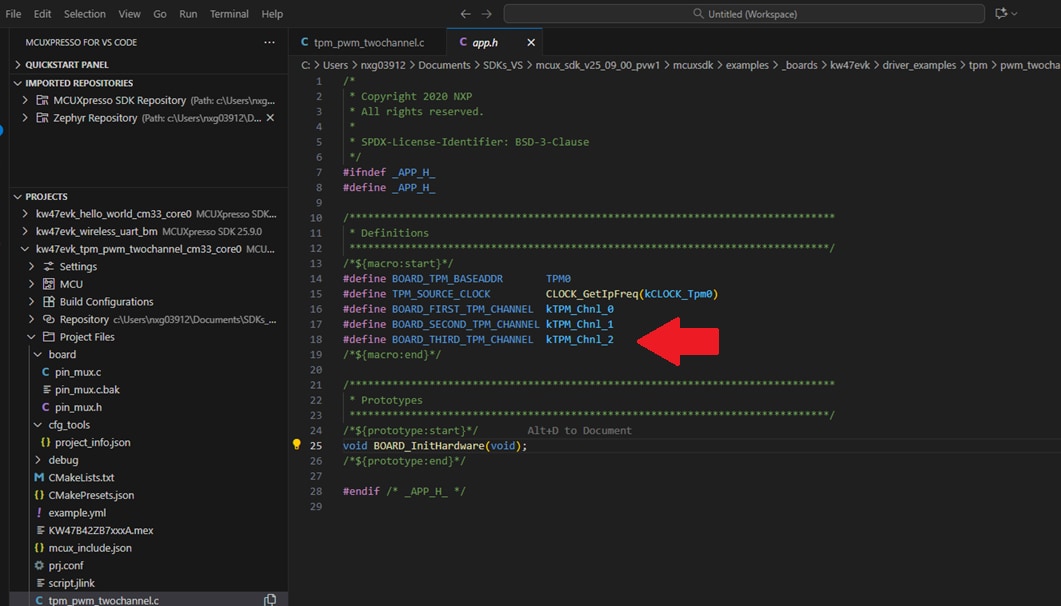
.mex). Search for the generatedpin_mux.candpin_mux.hsource files. Here you will replace the project's source files located on\mcuxsdk\examples\_boards\kw47evk\driver_examples\tpm\pwm_twochannelwith the newly generated source files. - Add the macro to enable the use of the
TPM0channel 2 in theapp.hsource file. - Next, you will add the neccessary code to enable
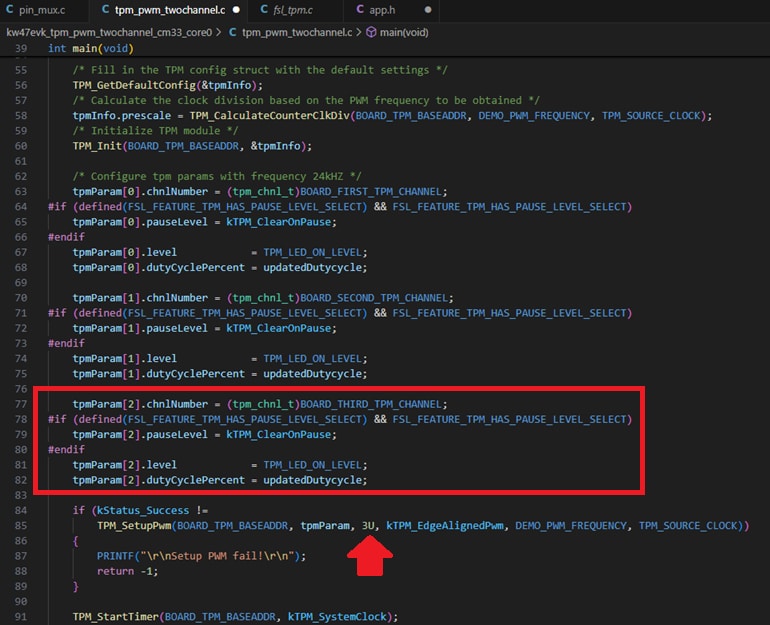
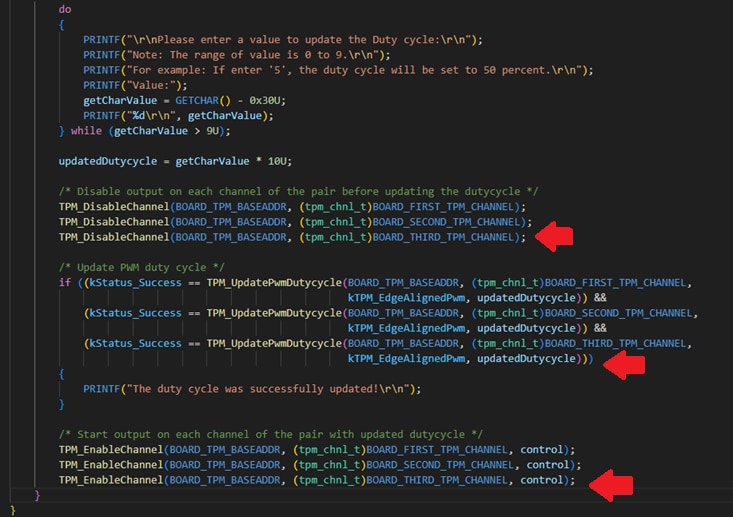
TPM0Channel 2. To edit thetpm_pwm_twochannel.ccode, use the following images as reference. - Build and download the project as done in the previous section.
- Run the application. You should now see a white colored RGB LED. Use the serial monitor to adjust brightness.
- Terminate the debug session.
5. MCUXpresso Developer Experience
Check out each of the following sections to learn about the ecosystem provided for flexible protyping and development. The video below we will introduce you to the FRDM platform, the full-featured EVK and the compatible shields for extended capabilities. In addition the presentation we will walk you through our Application Code Hub (ACH) portal where numerous application examples are provided through NXP's GitHub.
5.1 FRDM Platform, Full Feature EVK and Shields
For quick prototyping platforms, you have the option of the low-cost FRDM platform or the full-featured EVK.
FRDM development boards come with standard form factor and headers, easy access to MCU I/Os, on-board MCU-Link debugger and a USB-C cable. Our full-featured evaluation kits include extended I/O and interface access, extendibility with Wi-Fi and additional MCU-Link features. There are also many compatible Click Boards and/or Arduino shields. For devices supported by an Open CMSIS Pack, examples may be available on ACH. If not, many of them are easy to use via serial interface like inter-integrated circuit (I²C), serial peripheral interface (SPI), and universal asynchronous receiver/transmitter (UART), for which we provide drivers with examples in the MCUXpresso SDK.
5.2 Application Code Hub
The ACH further enhances our MCUXpresso Developer Experience by giving you an interactive dashboard to quickly locate software. Visit the ACH today to start exploring or discover additional details and benefits of the new interactive Application Code Hub.
Software in the ACH is located in NXP’s GitHub repository so it can be easily accessed and cloned from that location directly.
5.3 Demo Walkthrough
The following demo walks you through importing a project from ACH using a system based on the FRDM platform with a motor control shield and a low-cost LCD. Although your evaluation board may differ from this system, the following steps can be applied for all supported platforms.
Design Resources
Support
Forums
On this page
- 2.1
Install Your Toolchain
- 2.2
Jump Start Your Design
- 2.3
MCUXpresso Config Tools
- 2.4
Programming and Provisioning Tools
- 3.1
Updating NBU for Wireless Examples
- 3.2
Build and Flash Application using MCUXpresso for VS Code IDE
- 3.3
Build and Flash Application with Alternative Toolchains