Getting Started with the MCU Bootloader for NXP microcontrollers
Contents of this document
-
Plug It In
-
Get Software
-
Install and Import
Sign in to save your progress. Don't have an account? Create one.

Purchase your MCU Bootloader for NXP Microcontrollers
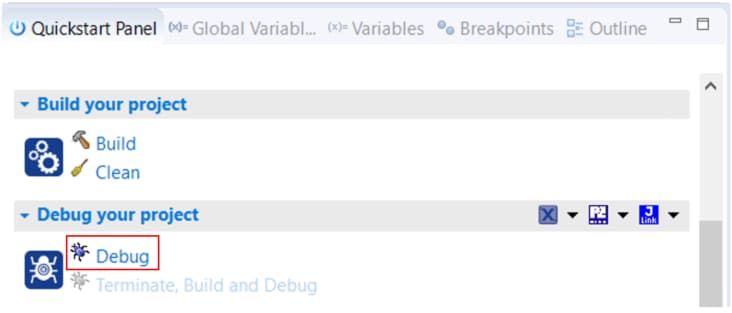
1. Plug It In
1.1 Select a board
Take FRDM-K64F as an example for demo.
1.2 Plug it in
Connect the board to the PC via the USB cable between the OpenSDA USB port on the board and the USB connector on the PC.
1.3 OpenSDA
Kinetis MCU boards are supplied with OpenSDA firmware pre-loaded. For software development on the MCU board, make sure the latest OpenSDA driver is on the FRDM development board. This allows debugging, flash programming and serial communication over a USB cable. Find the latest OpenSDA firmware for the boards here:
OpenSDA Update to the boardsFor the example, FRDM-K64F, go to this website and choose board FRDM-K64F to get the latest OpenSDA firmware.
1.4 PC Configuration
The output data from the provided example applications are provided over the MCU UART. This requires that the driver for the board’s virtual COM port is installed. The board MUST be plugged into the PC before the driver installer is run.
The links for the latest OpenSDA Windows serial port drivers are provided on the same web:
OpenSDA Update to the boardsFor the example, FRDM-K64F, go to this website and choose board FRDM-K64F. In the coming webpage, click on Arm CMSIS-DAP serial drivers to download Windows Serial Port Drivers.
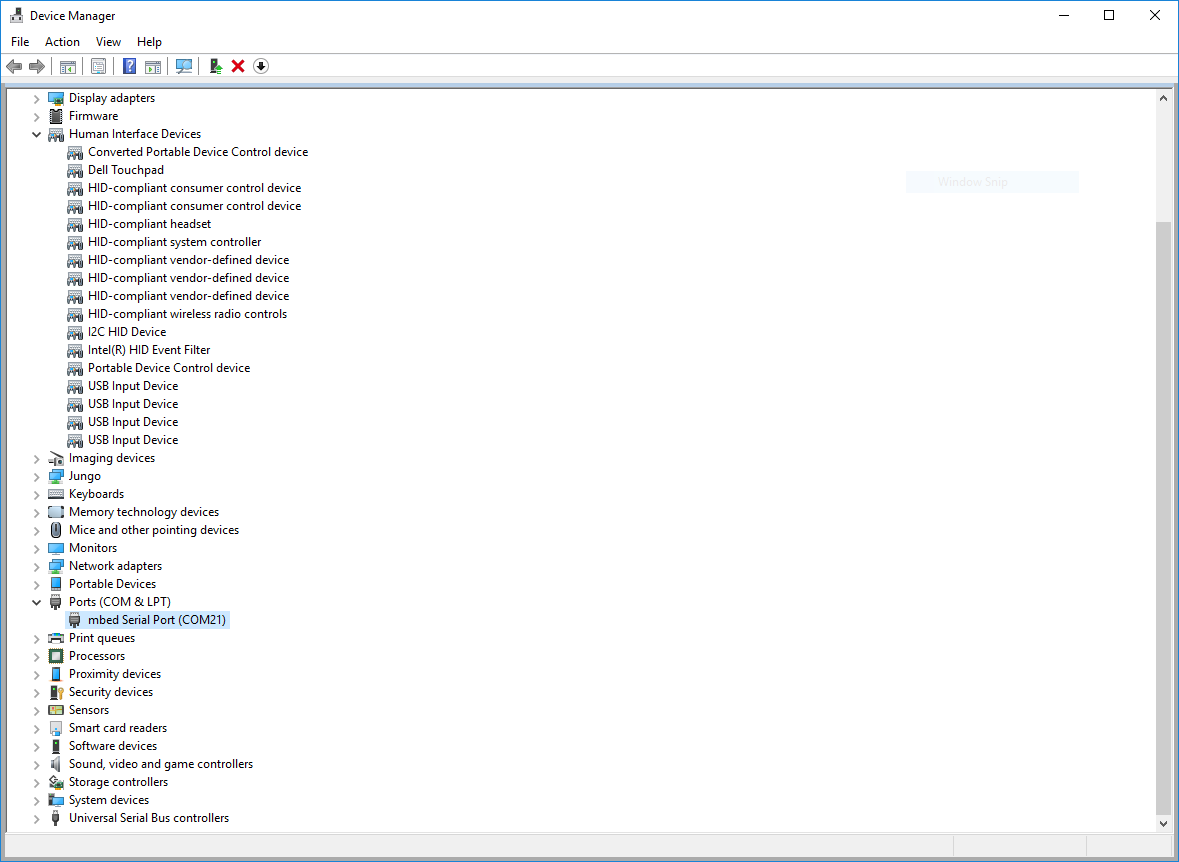
Once the Windows Serial Port Drivers are installed on the PC, determine the port number of the FRDM board’s virtual COM port by opening the device manager and looking under the "Ports" group.
Note: All the Serial Port Drivers are included and installed automatically when installing MCUXpresso IDE. Skip this step and jump to section 2 if MCUXpresso IDE is planned to install.
The demonstration board is now ready to communicate with the PC.
2. Get Software
2.1 Get MCU Bootloader
- Choose desired device part number from the drop down menu below.
- Click on the appropriate OS type, which will begin steps for downloading.
Download MCU Bootloader
Choose Part Number
- For this example, FRDM-K64F board, Windows OS, MCUXpresso IDE, middleware MCUBOOT and USB stack are selected.
2.2 Build the SDK
Click on Download SDK. A pop-up window SDK Download will show when the package is built successfully. Click on Download SDK Archive to download the package. The package is provided as a zip file.
2.3 Install Your Toolchain
NXP offers a complimentary toolchain called MCUXpresso IDE.
 Get MCUXpresso IDE
Get MCUXpresso IDE
Want to use a different toolchain?
No problem! The MCUXpresso SDK includes support for other tools such as IAR, Keil.

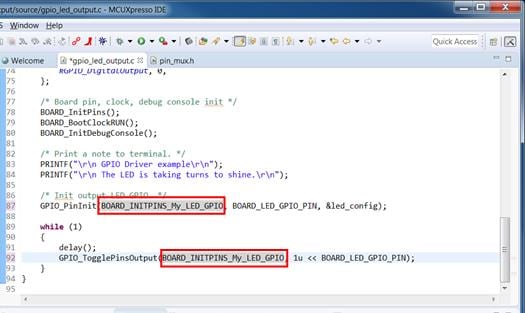
3. Install and Import
3.1 Install and Import
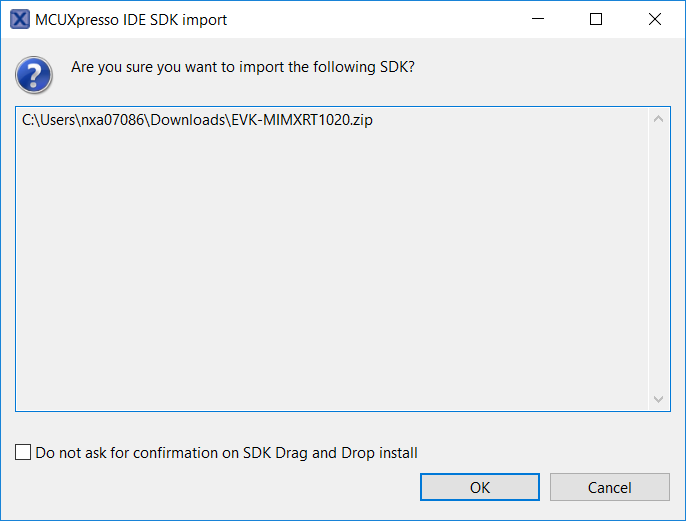
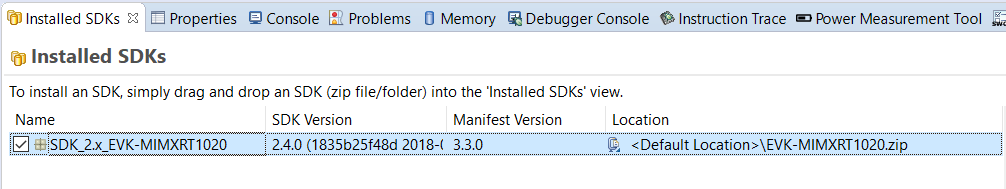
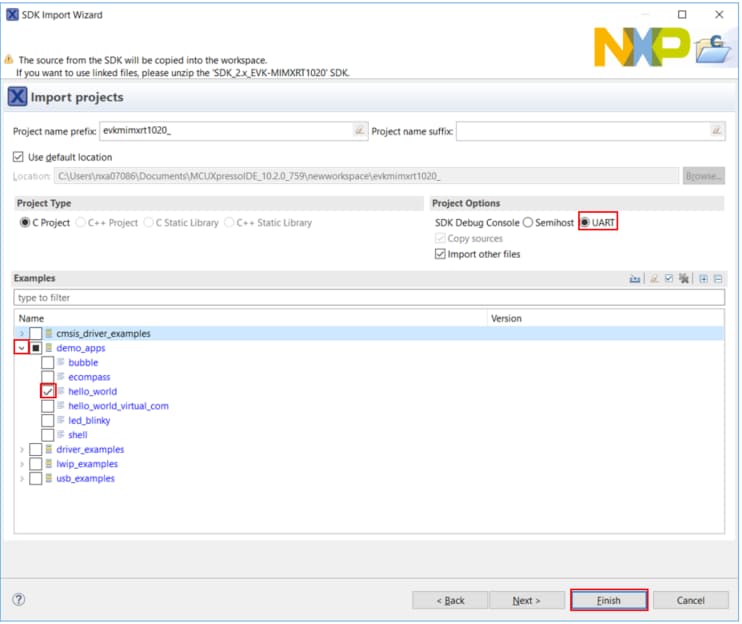
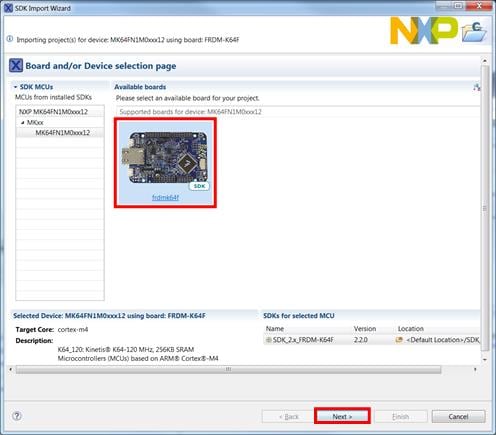
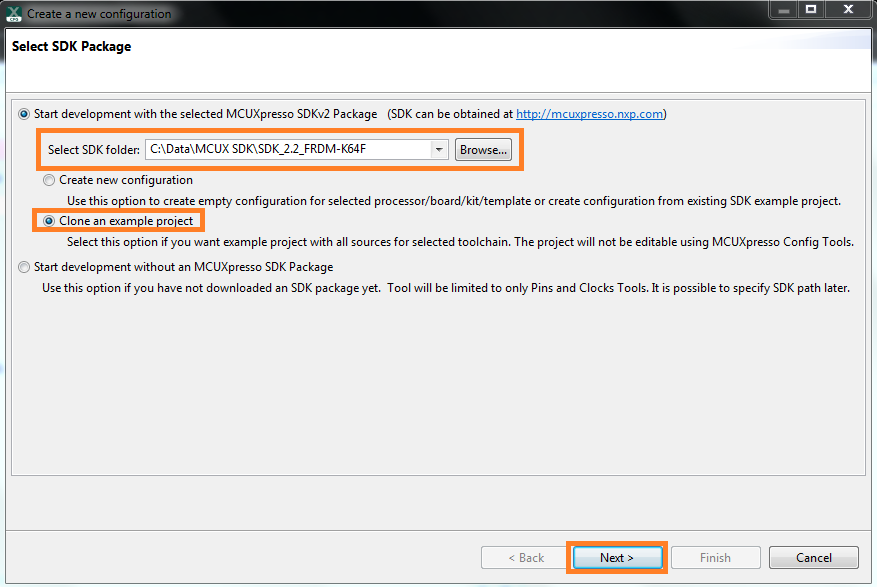
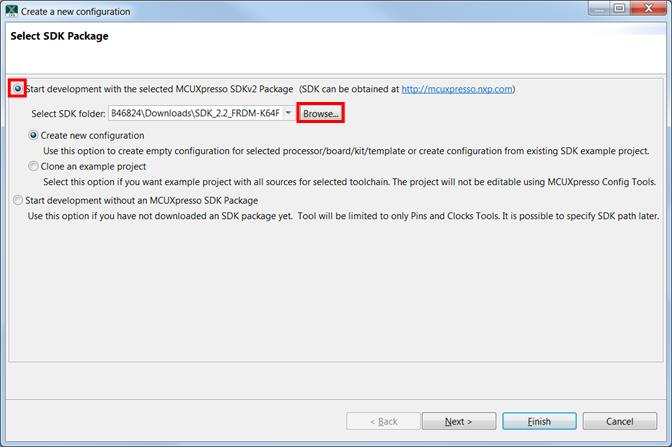
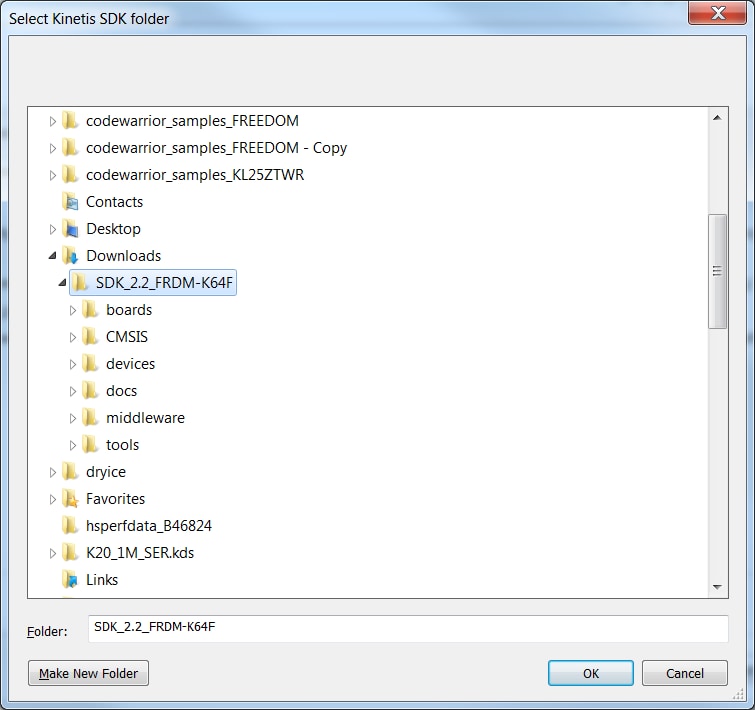
Install the downloaded FRDM-K64F SDK package into MCUXpresso IDE (Simply drag and drop the zipped SDK package as it is to the “Installed SDKs” view).
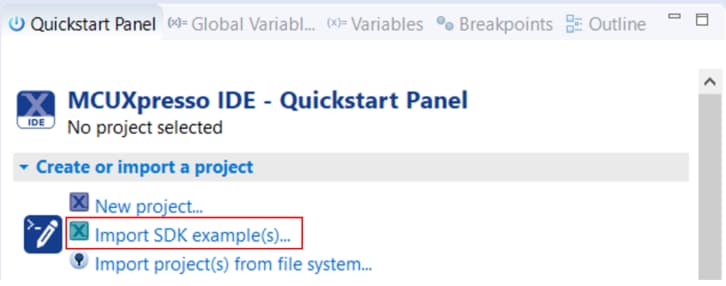
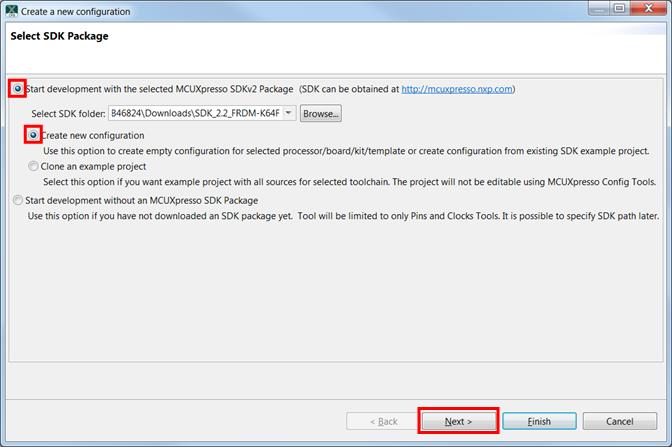
Once the SDK installation is completed, click on ‘Import SDK examples’.
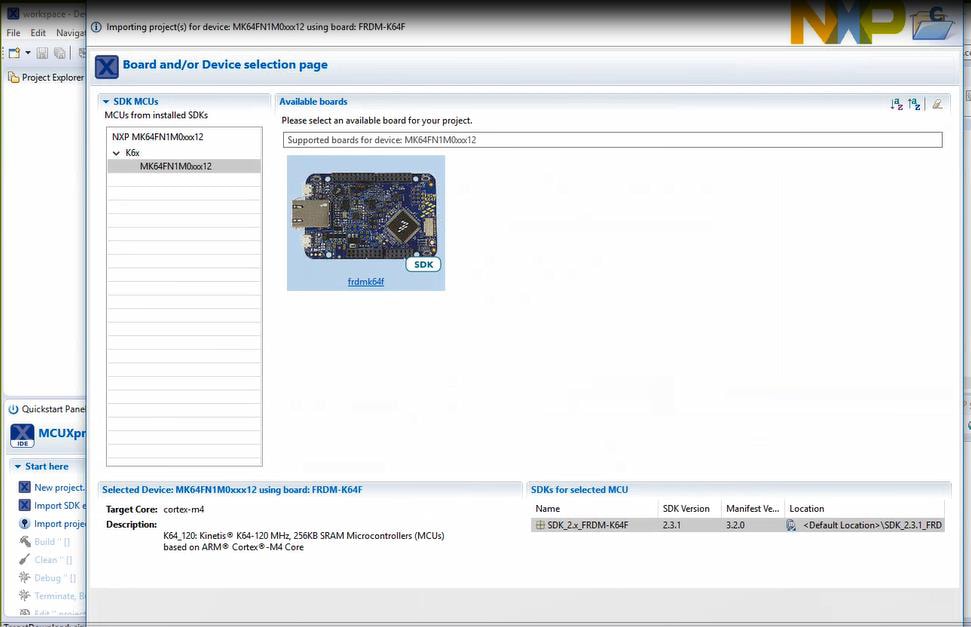
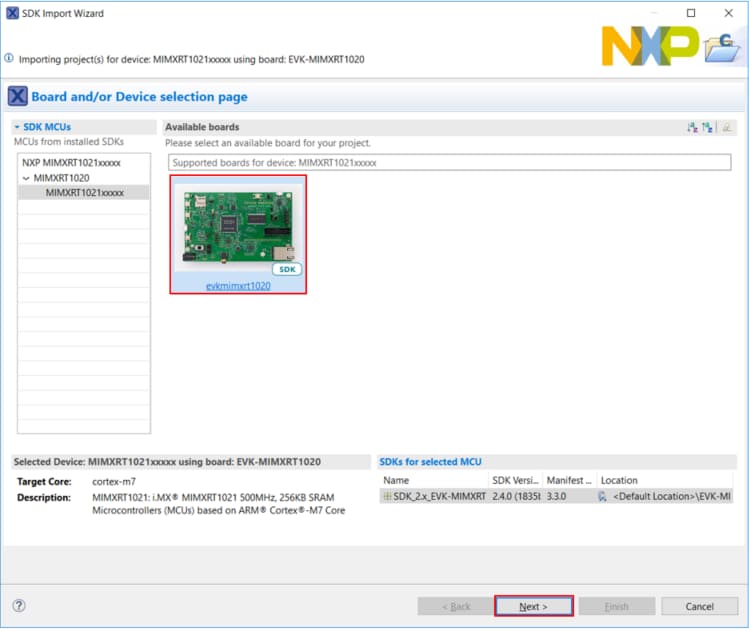
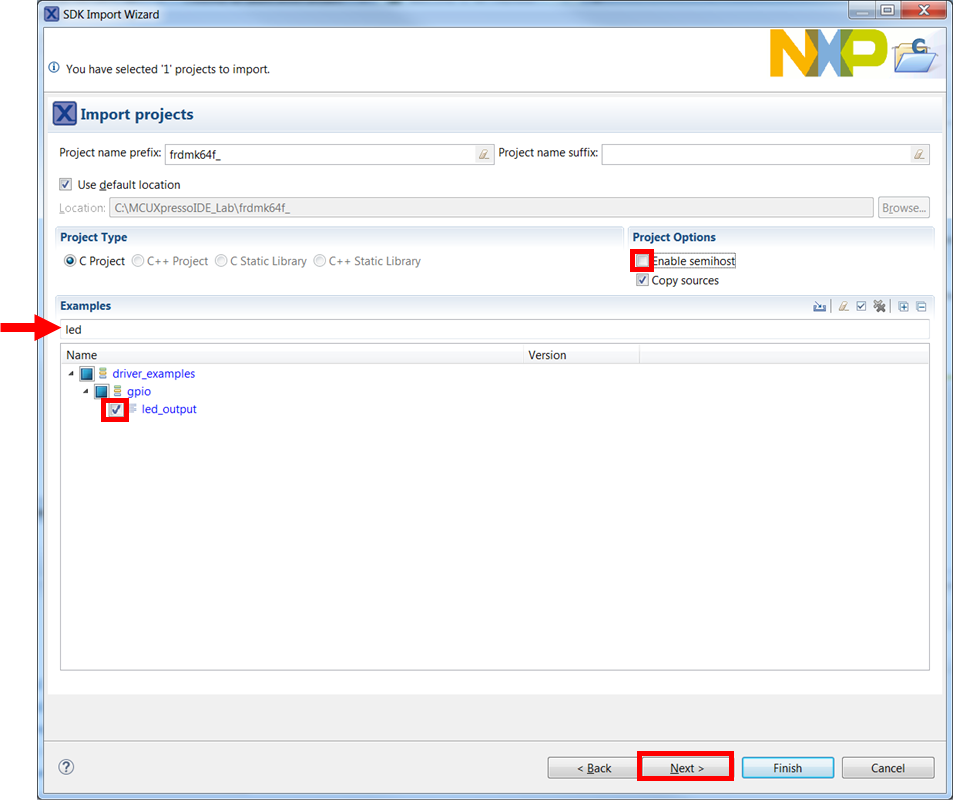
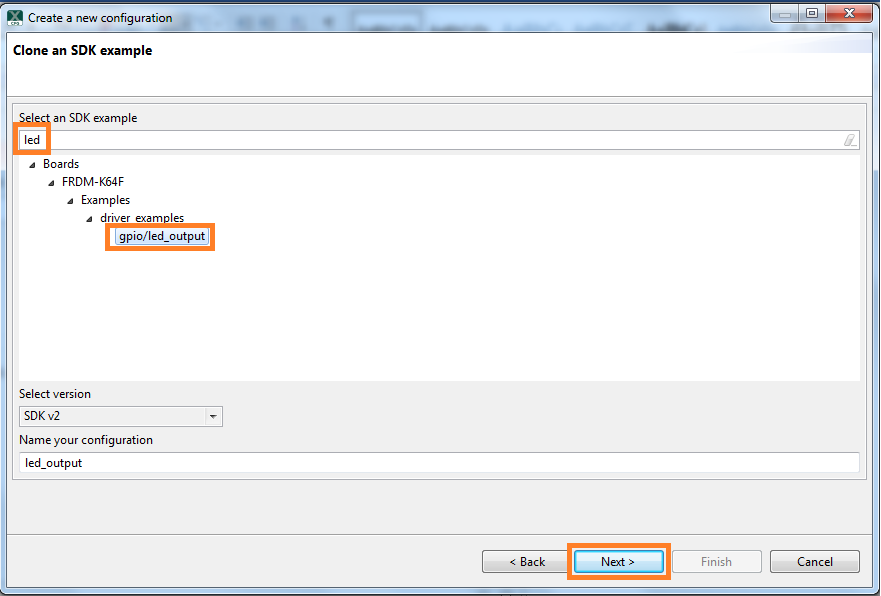
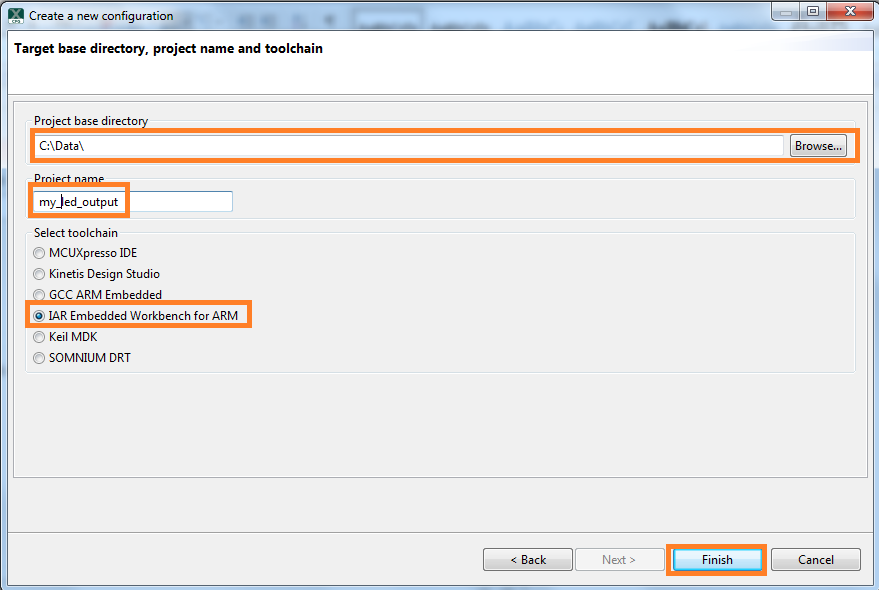
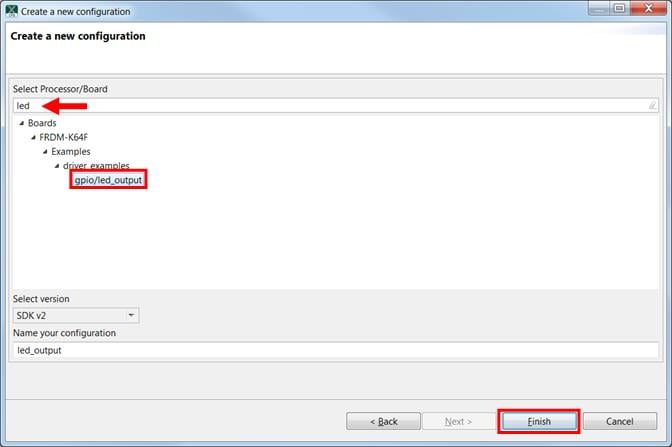
Import freedom_bootloader example from the list of available projects.
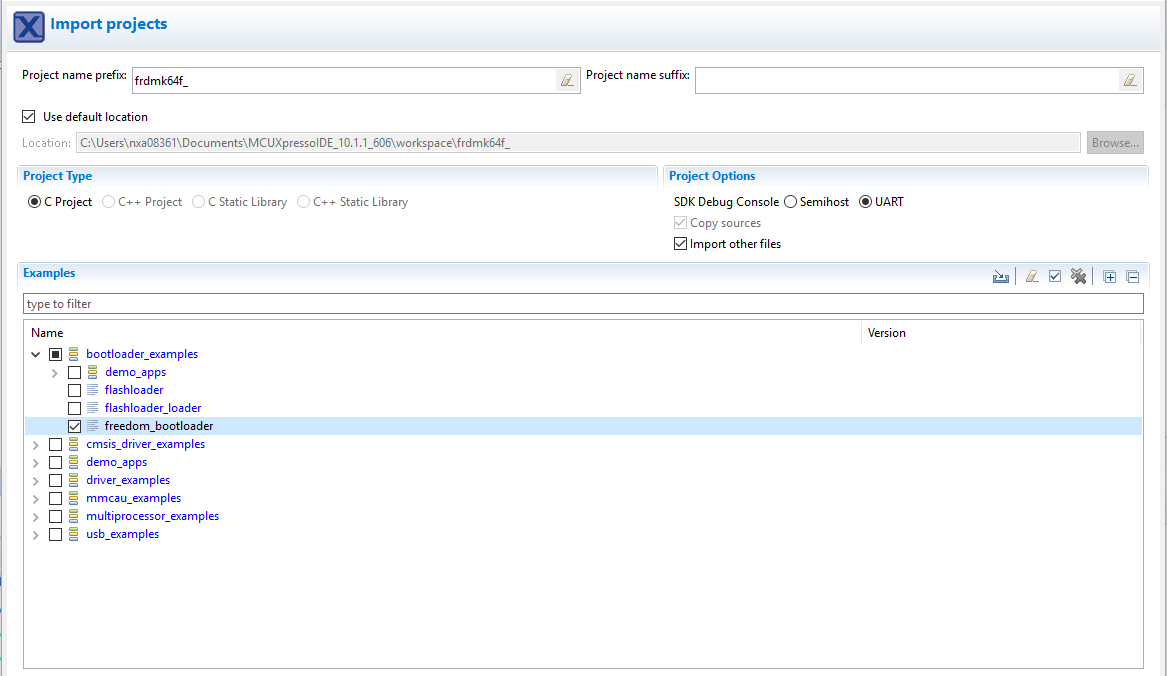
Note: Once, the freedom_bootloader example is imported successfully, the MCUXpresso IDE automatically creates the corresponding standalone project in your workspace.
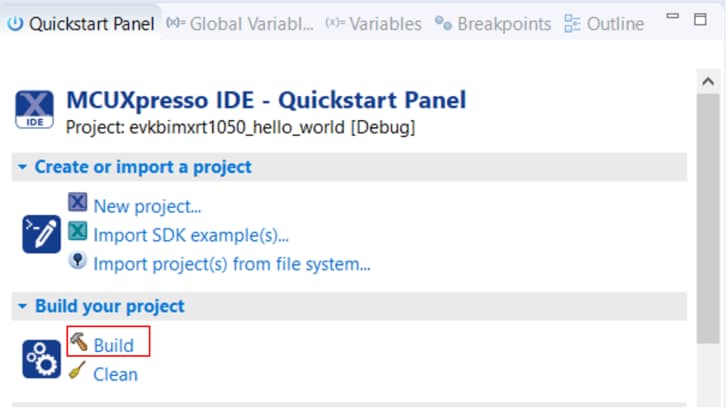
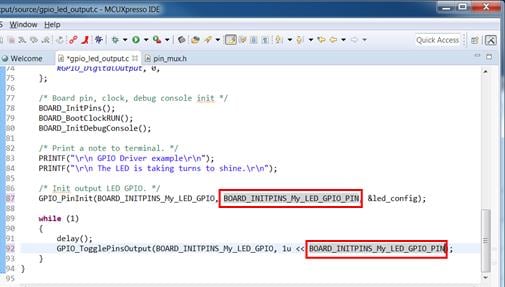
3.2 Build and Load
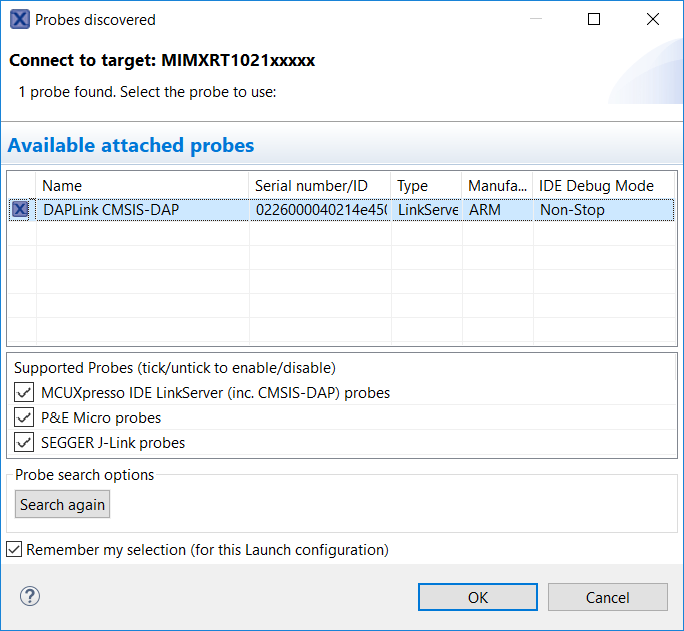
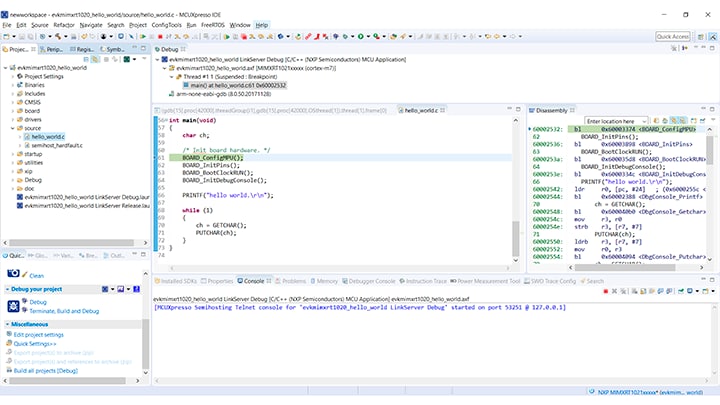
Build the project by clicking 'build' button.
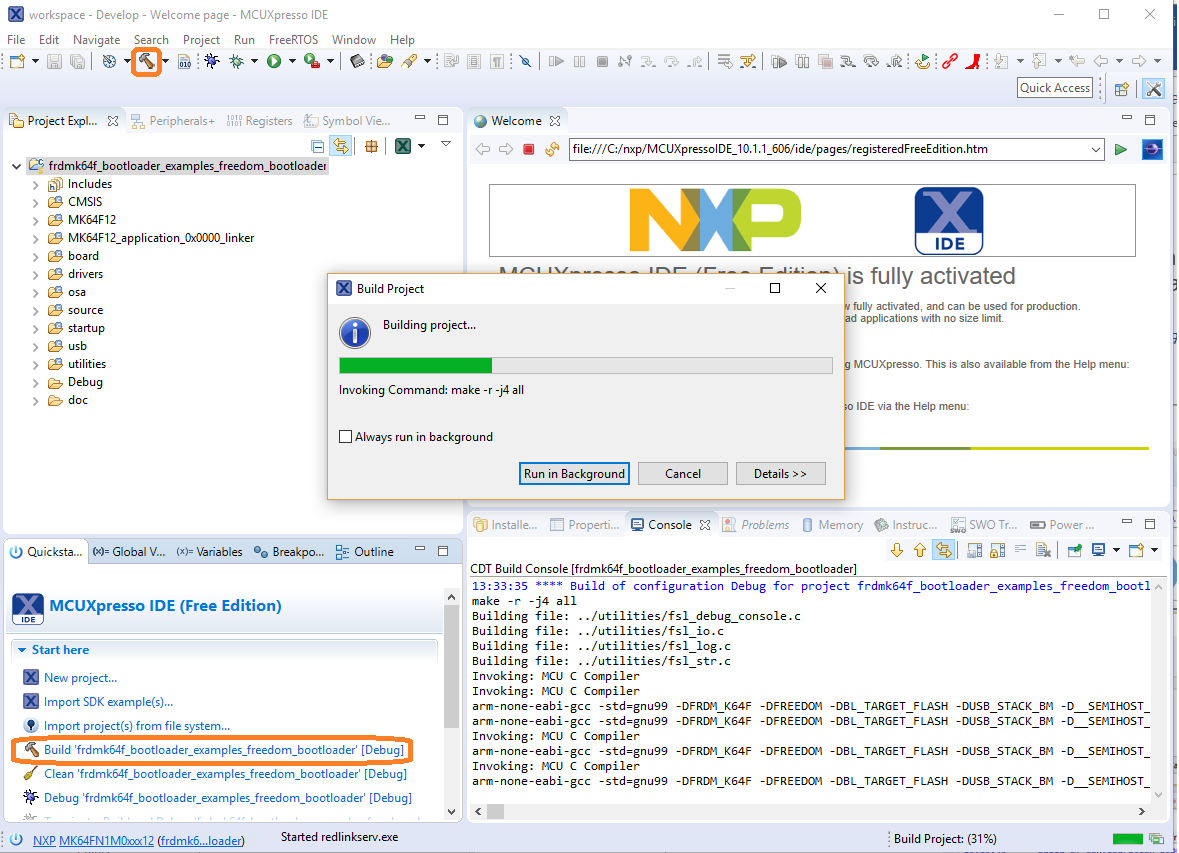
Load firmware by clicking on “Debug frdmk64fxx”
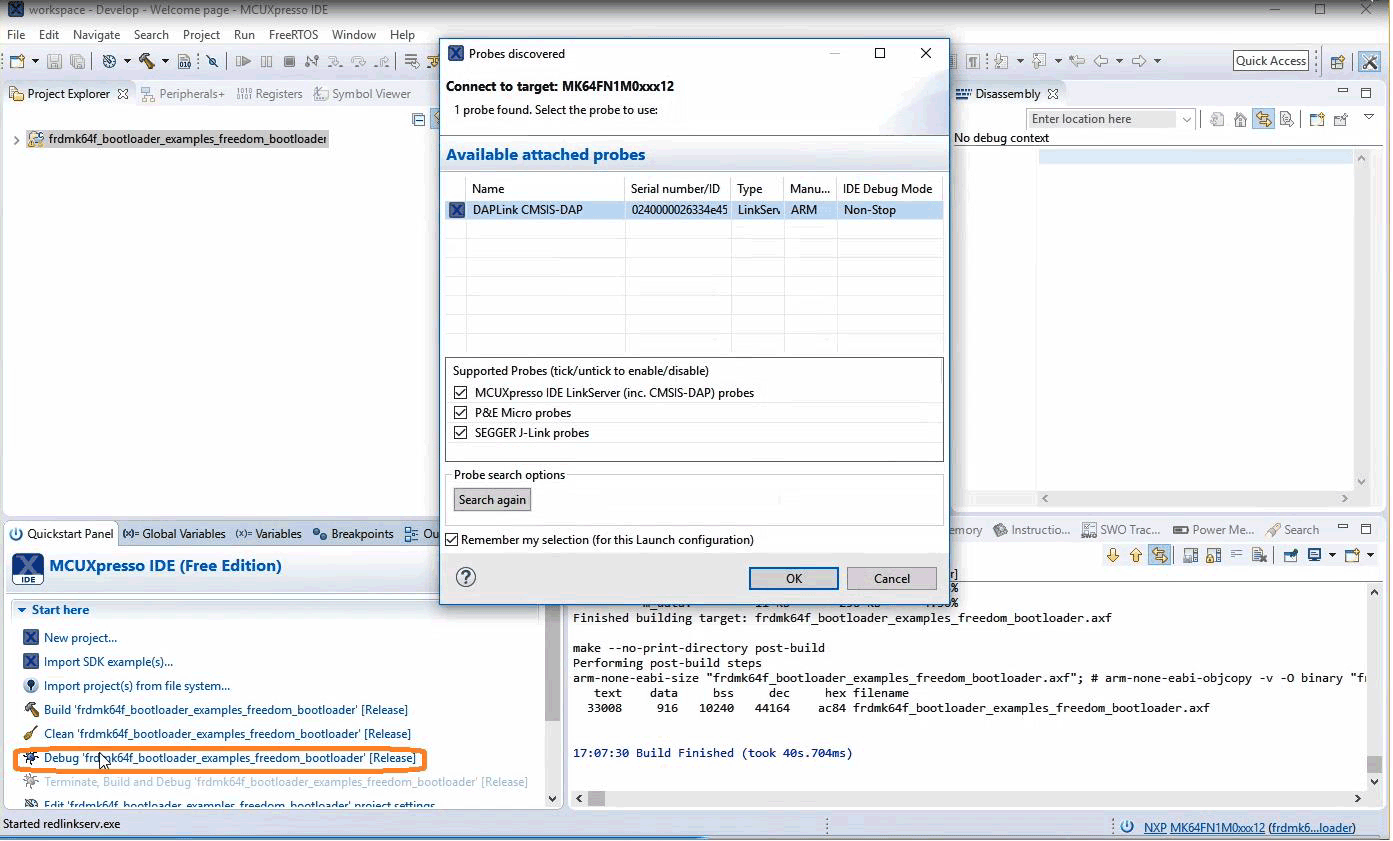
3.3 Run blhost
Before running blhost, get the port number of the FRDM board’s virtual COM port by opening the device manager and looking under the "Ports" group.
In downloaded package, Windows blhost is located at
middleware\mcu-boot\bin\Tools\blhost\win.
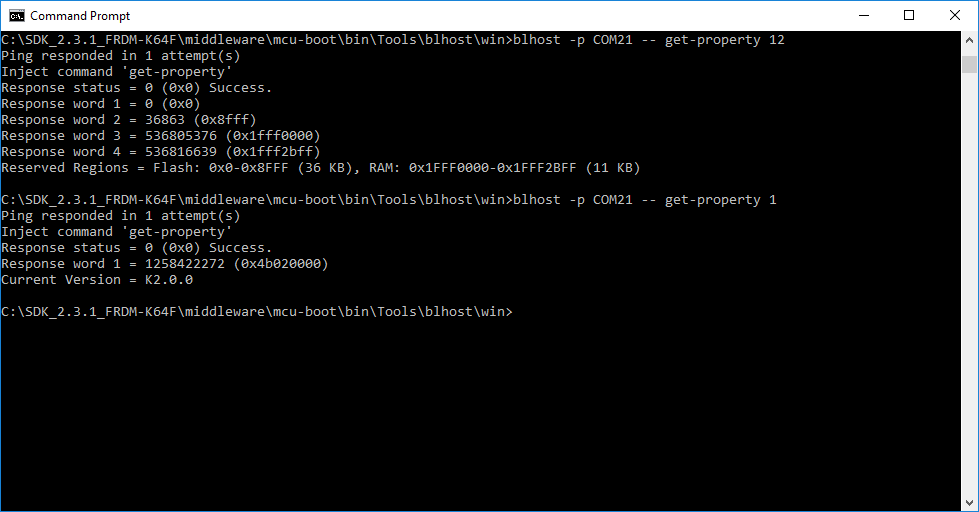
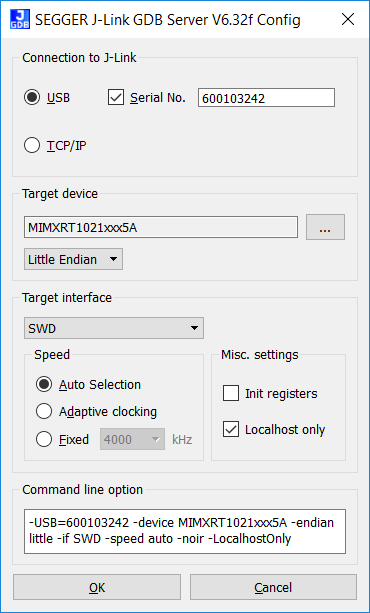
Open a command prompt and run blhost to initiate communication and inject commands to the bootloader. For instance, you can connect to bootloader over UART with an option "-p" and run blhost command get-property to get some information from bootloader.
Type blhost -p COM21 -- get-property 12 to get memory regions reserved by the Bootloader.
Type blhost -p COM21 -- get-property 1 to get current bootloader version.
For more details, please refer to blhost User’s Guide.