Getting Started with the S32K144EVB
Contents of this document
-
Out of the Box
-
Get Software
-
Plug It In
-
Build, Run
-
Debug
Sign in to save your progress. Don't have an account? Create one.
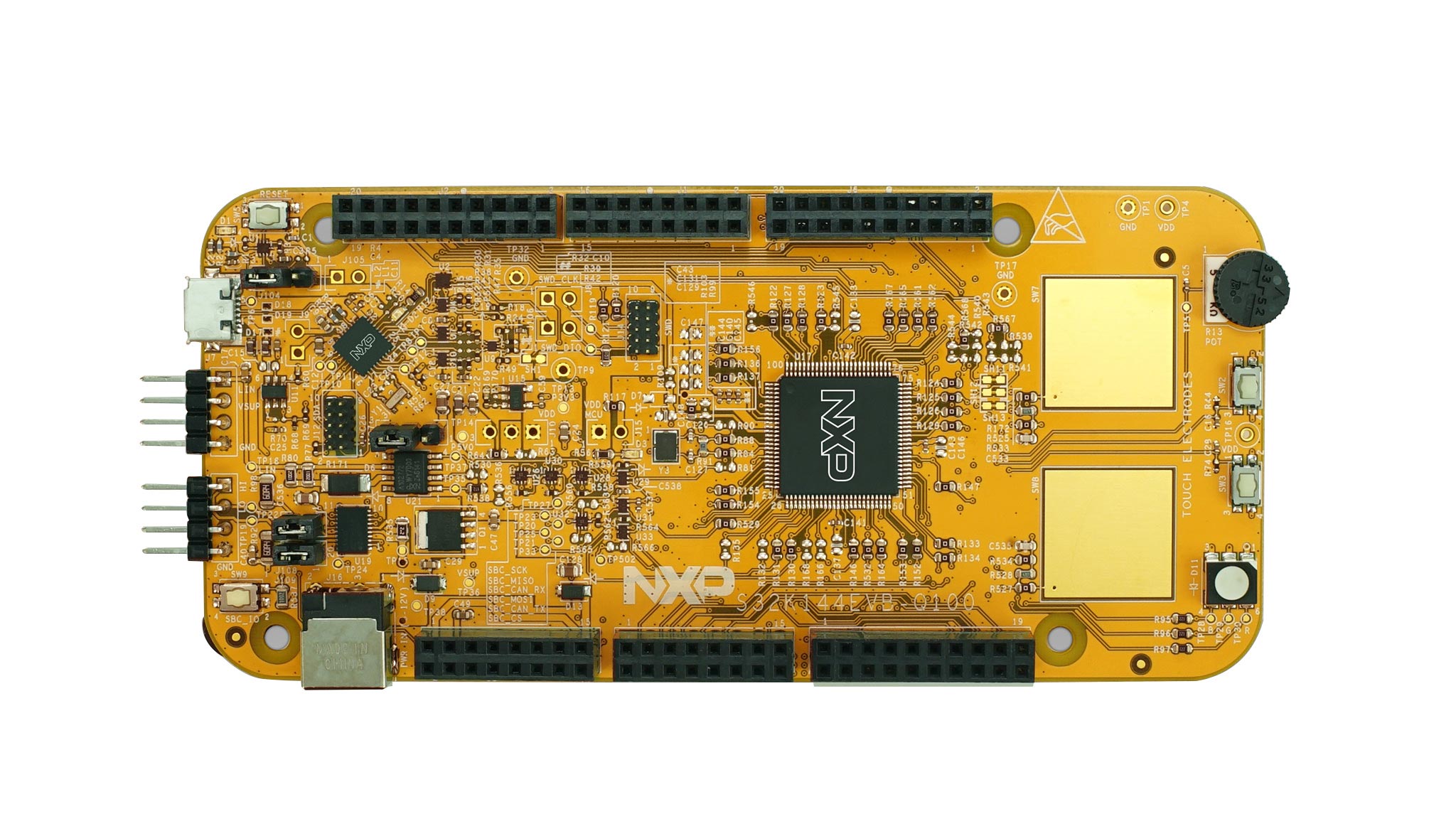
Purchase your S32K144-Q100 Evaluation Board for Automotive General Purpose
1. Out of the Box
Applies for the S32K144EVB evaluation board (REV B)
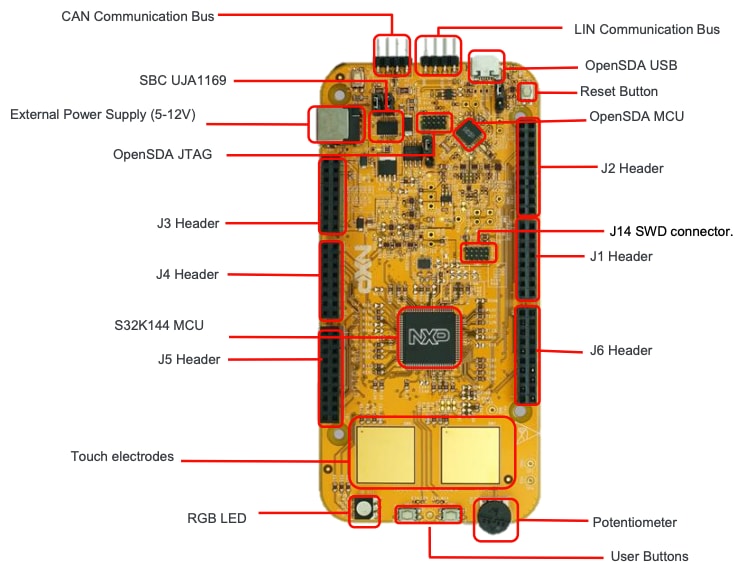
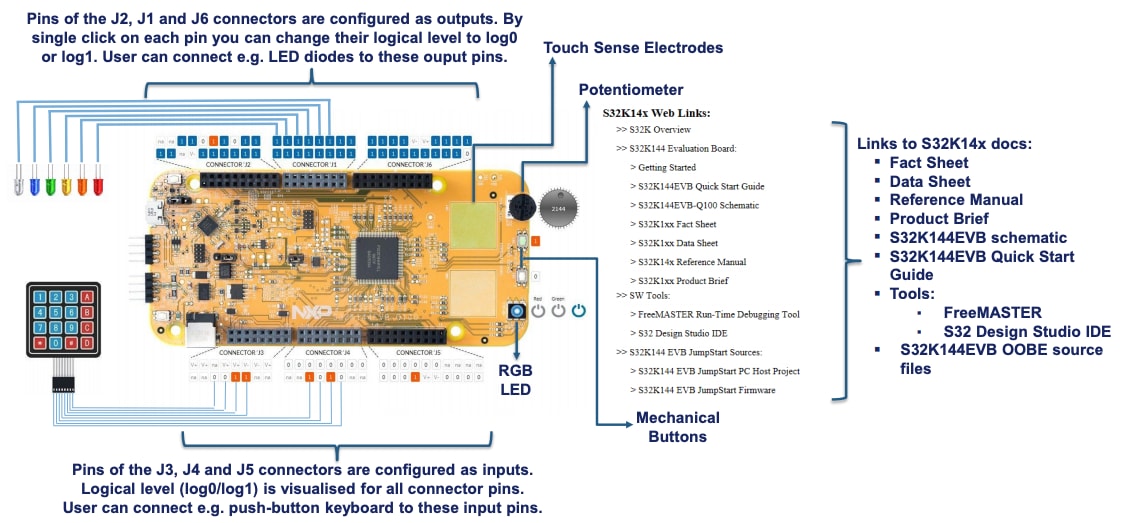
1.3 Understanding the HMI Mapping
| Component | S32K144 |
|---|---|
| Red LED | PTD15 (FTM0 CH0) |
| Blue LED | PTD0 (FTM0 CH2) |
| Green LED | PTD16 (FTM0 CH1) |
| Potentiometer | PTC14 (ADC0_SE12) |
| SW2 | PTC12 |
| SW3 | PTC13 |
| OpenSDA UART Tx | PTC7 (LPUART1_TX) |
| OpenSDA UART Rx | PTC6 (LPUART1_RX) |
| CAN Tx | PTE5 (CAN0_TX) |
| CAN Rx | PTE4 (CAN0_RX) |
| LIN Tx | PTD7 (LPUART2_TX) |
| LIN Rx | PTD6 (LPUART2_RX) |
| SBC_SCK | PTB14 (LPSPI1_SCK) |
| SBC_MISO | PTB15 (LPSPI1_SIN) |
| SBC_MOSI | PTB16 (LPSPI1_SOUT) |
| SBC_CS | PTB17 (LPSPI1_PCS3) |
2. Get Software
2.1 Integrated Development Environment (IDE)
S32K144EVB evaluation board performs better when using S32 Design Studio for Arm®.
2.2 Run-Time Debugging Tool
S32K144EVB evaluation board performs better when using the FreeMASTER tool for run-time debugging. You can also download and install the FreeMASTER Communication Driver (source code already included in the example project).
DOWNLOAD FreeMASTER Tool3. Plug It In
3.1 Set Up Jumpers in S32K144EVB Evaluation Board
| Jumper | Setting | Description |
|---|---|---|
J104 |
1-2 | Reset signal to OpenSDA, use to enter into OpenSDA Bootloader mode. |
| 2-3 (Default) | Reset signal direct to the MCU, use to reset S32K144. | |
J107 |
1-2 | S32K144 powered by 12 V power source. |
| 2-3 (Default) | S32K144 powered by USB micro connector. | |
J109/J108 |
1-2 (Default) | Removes CAN termination resistor. |
Watch the video or use the step-by-step guide, below.
3.2 Plug In the 12 V Power Supply
The S32K144EVB evaluation board powers from a USB or external 12 V power supply. By default USB power is enabled with J107 jumper (2-3 closed).
Connect the USB cable to a PC using a USB cable and connect other end of USB cable (microUSB) to mini-B port on to J7 on your S32K144EVB.
Allow the PC to automatically configure the USB drivers if needed. Debug is done using OpenSDA through J7.
Once the board is recognized, it should appear as a mass storage device in your PC with the name EVB-S32K144.
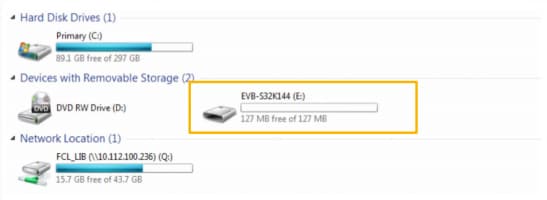
The S32K144EVB evaluation board is preloaded with a software in which red, blue and green LEDS will toggle at different rates:
4. Build, Run
Let’s take it for a test drive.
4.1 Communicate with Run-Time Debugger
-
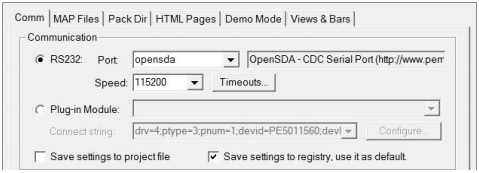
Manually = Project → Options → Comm
-
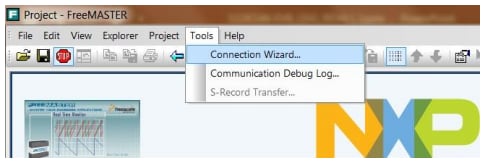
Automatically = Tools → Connection Wizard
Learn more about OpenSDA at Projects and Tutorials.
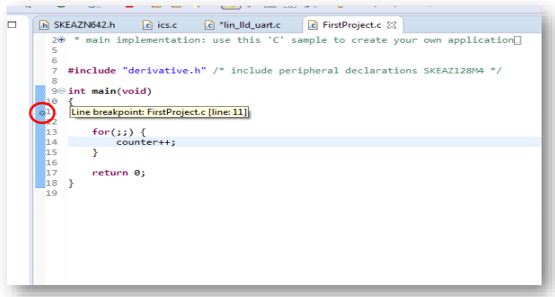
4.3 Import and Debug the Project to IDE
Watch the video to create a new project and load a code example to blink an LDE. The video also covers hoe to build and debug your project. You can also use the step-by-step guide.
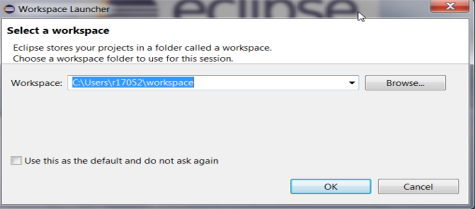
Launch the S32 Design Studio for Arm and select a default Workspace or specify a new one, then click OK.
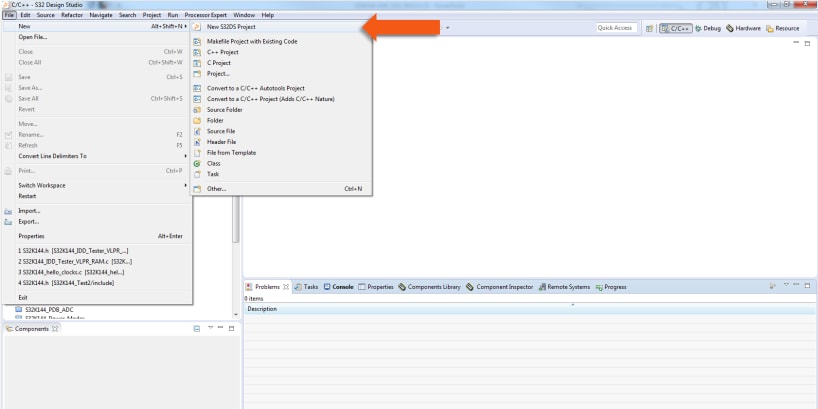
To create a new project, select File → New → Project
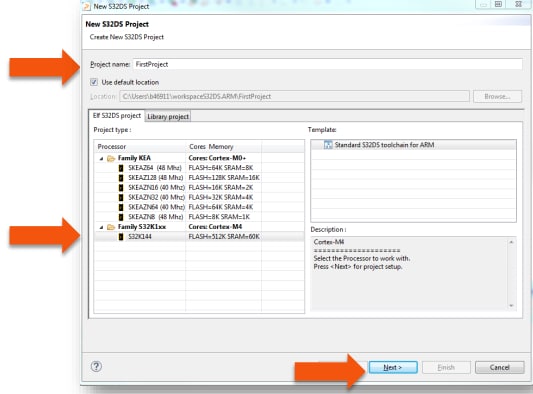
Choose a project name and then select a project type, then click Next.
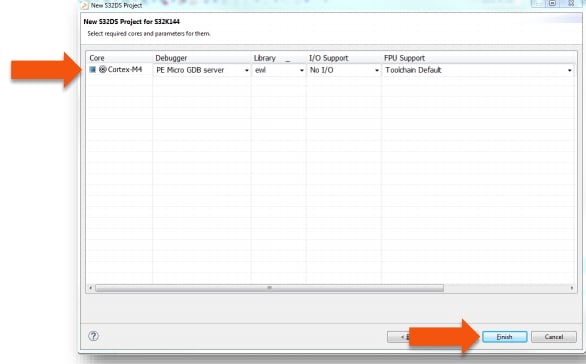
Select Debugger and Library, then click Finish.
4.4 Set Up Debug Configuration
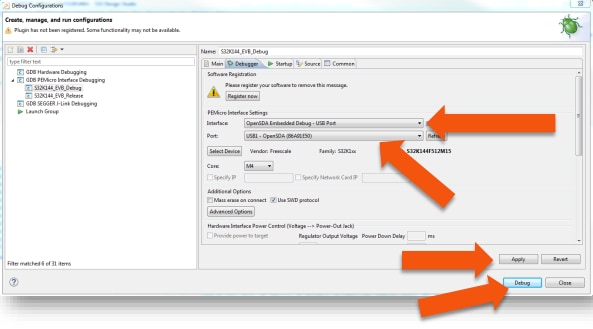
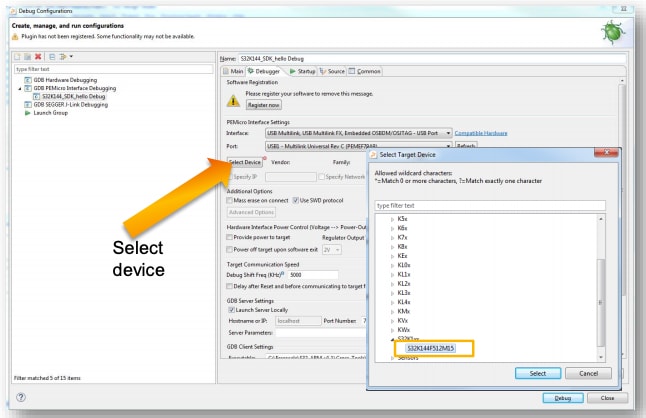
Select OpenSDA to debug with it.
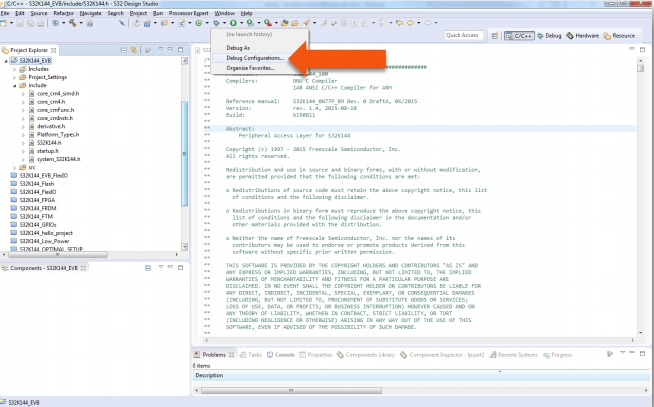
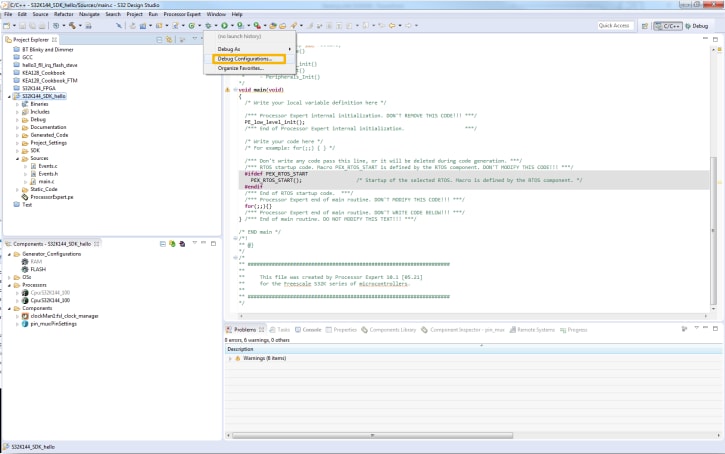
Select your project, and click on "Debug Configuration".
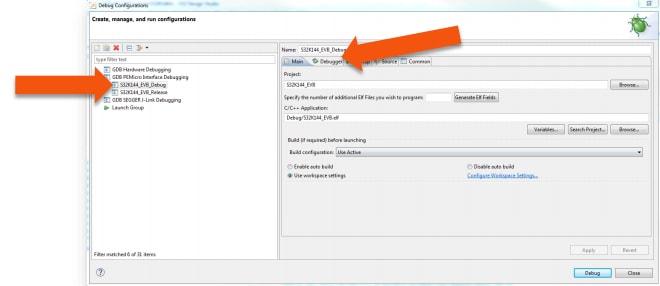
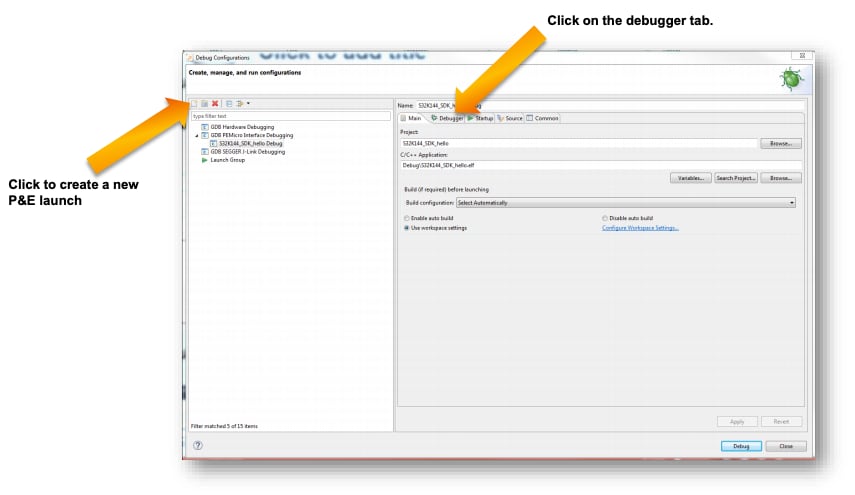
Select the debug configuration under "GDB PEMicro" Interface Debugging, click the "Debugger" tab.
In "Interface", select OpenSDA. If your board is plugged in, it should appear in "Port". To finish, click "Apply" then "Debug".
5. Debug
5.1 Debug Basics
Step, Run, Suspend, Resume
Step Into (F5)
Step Over (F6)
Step Return (F7)
Run
Suspend
Resume (F8)
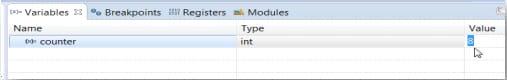
5.2 View Variables
Click the Variables tab. To enter different values, click in the Value field.
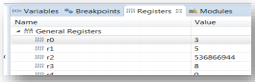
5.3 View and Alter Registers
To see CPU registers, click the Registers tab. To enter different values, click in the Value field.
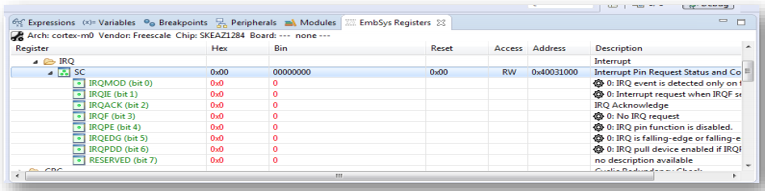
View peripheral registers in the EmbSys Registers tab:
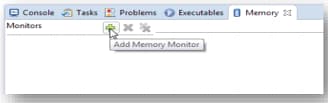
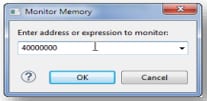
5.4 View and Alter Memory
Select Add Memory Monitor and then select the base address to: 40000000
5.5 View Memory
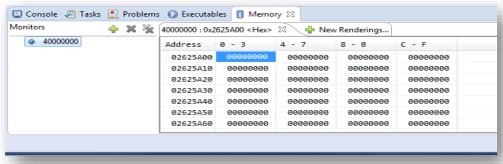
5.7 Reset and Terminate the Debug Session
To reset the program counter, select Terminate (Ctrl+F2).
5.8 Debug with FreeMASTER
Debug configuration is only required once. Subsequent starting of debugger does not require those steps.
There are three options to start debugging:
- If the Debug Configuration is still open, click Debug on the bottom right.
-
Select Run → Debug (or hit F11)
-
Select the bug icon and select
…_debug.elftarget
Learn more about debugging basics at Projects and Tutorials.
FreeMASTER
FreeMASTER
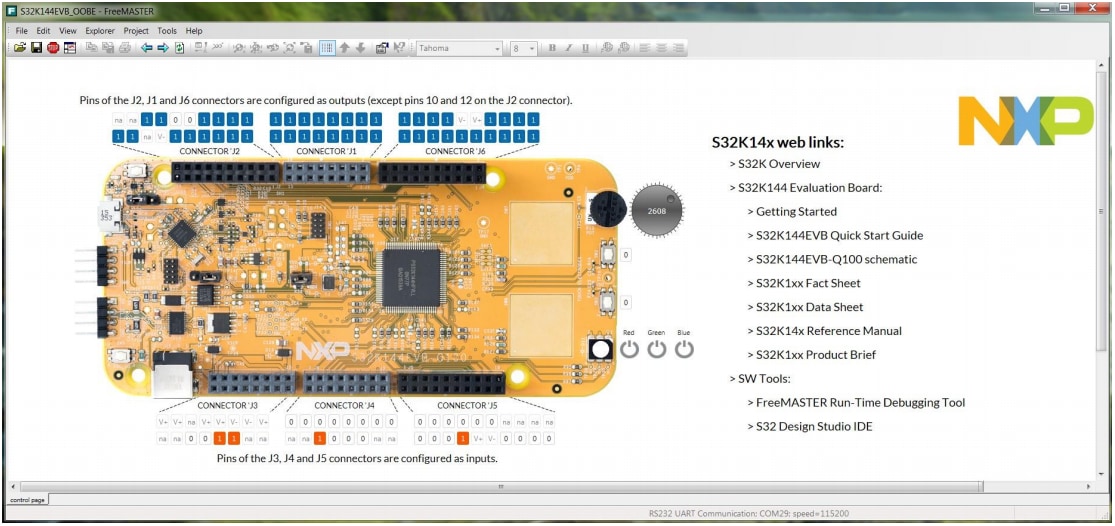
To display the main project panel, go to: Project → View → Project Tree
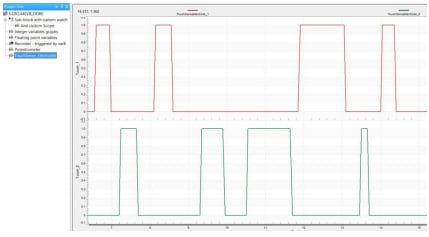
To display real-time oscilloscope graph examples, select Potentiometer or Touch Sense Electrodes:
- Analog values from potentiometer:
- Responses from touch sense electrodes:
OpenSDA
OpenSDA
OpenSDA is an open-standard serial and debug adapter. It bridges serial and debug communications between a USB host and an embedded target processor. OpenSDA software includes a flash-resident USB mass-storage device (MSD) bootloader and a collection of OpenSDA applications.
The S32K144EVB comes with the MSD Flash Programmer OpenSDA Application preinstalled.
Follow these instructions to run the OpenSDA Bootloader and update or change the installed OpenSDA Application.
| Enter OpenSDA Bootloader Mode | Load an OpenSDA Application |
|---|---|
A removable drive should now be visible in the host file system with a volume label of BOOTLOADER. You are now in OpenSDA Bootloader mode. |
You are now running the latest version of the MSD Flash Programmer. Use this same procedure to load other OpenSDA Applications. |
The MSD Flash Programmer is a composite USB application that provides a virtual serial port and an easy and convenient way to program applications into the KEA MCU. It emulates a FAT16 file system, appearing as a removable drive in the host file system with a volume label of EVB-S32K144. Raw binary and Motorola S-record files that are copied to the drive are programmed directly into the flash of the KEA and executed automatically. The virtual serial port enumerates as a standard serial port device that can be opened with standard serial terminal applications.
| Using the MSD Flash Programmer | Using the Virtual Serial Port |
|---|---|
The new application should now be running on the S32K144EVB. Starting with v1.03 of the MSD Flash Programmer, you can program repeatedly without the need to unplug and reattach the USB cable before reprogramming. Drag one of the |
|
Processor Expert
Processor Expert
Watch the video to create a new project and load a code example to make a blinking LED. The video also covers how to build and debug your project. You can also use the step-by-step guide.
RTD Examples
Kickstart your RTD journey with these handy examples. We've rounded up some of the most common use cases to get you inspired and moving forward.
Users can copy the path directly into their window once the RTD is downloaded.
RTD Examples
ADC
C:\NXP\S32DS.3.6.1\S32DS\software\PlatformSDK_S32K1_S32M24\RTD\Adc_TS_T40D2M30I0R0\examples\S32DS\S32K1\Adc_example_S32K144ADC PDB IP
C:\NXP\S32DS.3.6.1\S32DS\software\PlatformSDK_S32K1_S32M24\RTD\Adc_TS_T40D2M30I0R0\examples\S32DS\S32K1\Adc_Pdb_Ip_example_S32K144CAN
C:\NXP\S32DS.3.6.1\S32DS\software\PlatformSDK_S32K1_S32M24\RTD\Can_43_FLEXCAN_TS_T40D2M30I0R0\examples\S32DS\S32K1\Can_example_S32K144FLEX CAN IP
C:\NXP\S32DS.3.6.1\S32DS\software\PlatformSDK_S32K1_S32M24\RTD\Can_43_FLEXCAN_TS_T40D2M30I0R0\examples\S32DS\S32K1\FlexCAN_Ip_example_S32K144CRC
C:\NXP\S32DS.3.6.1\S32DS\software\PlatformSDK_S32K1_S32M24\RTD\Crc_TS_T40D2M30I0R0\examples\S32DS\S32K1\Crc_Example_S32K144CRC IP
C:\NXP\S32DS.3.6.1\S32DS\software\PlatformSDK_S32K1_S32M24\RTD\Crc_TS_T40D2M30I0R0\examples\S32DS\S32K1\Crc_Ip_Example_S32K144DIO
C:\NXP\S32DS.3.6.1\S32DS\software\PlatformSDK_S32K1_S32M24\RTD\Dio_TS_T40D2M30I0R0\examples\S32DS\S32K1\Dio_Example_S32K144GPIO DIO IP
C:\NXP\S32DS.3.6.1\S32DS\software\PlatformSDK_S32K1_S32M24\RTD\Dio_TS_T40D2M30I0R0\examples\S32DS\S32K1\Gpio_Dio_Ip_Example_S32K144EEP
C:\NXP\S32DS.3.6.1\S32DS\software\PlatformSDK_S32K1_S32M24\RTD\Eep_TS_T40D2M30I0R0\examples\S32DS\S32K1\Eep_Example_S32K144FTFC EEP IP
C:\NXP\S32DS.3.6.1\S32DS\software\PlatformSDK_S32K1_S32M24\RTD\Eep_TS_T40D2M30I0R0\examples\S32DS\S32K1\Ftfc_Eep_Ip_Example_S32K144FEE
C:\NXP\S32DS.3.6.1\S32DS\software\PlatformSDK_S32K1_S32M24\RTD\Fee_TS_T40D2M30I0R0\examples\S32DS\S32K1\Fee_Example_S32K144FLS
C:\NXP\S32DS.3.6.1\S32DS\software\PlatformSDK_S32K1_S32M24\RTD\Fls_TS_T40D2M30I0R0\examples\S32DS\S32K1\Fls_Example_S32K144FTFC IP
C:\NXP\S32DS.3.6.1\S32DS\software\PlatformSDK_S32K1_S32M24\RTD\Fls_TS_T40D2M30I0R0\examples\S32DS\S32K1\Ftfc_Ip_Example_S32K144FTM GPT
C:\NXP\S32DS.3.6.1\S32DS\software\PlatformSDK_S32K1_S32M24\RTD\Gpt_TS_T40D2M30I0R0\examples\S32DS\S32K1\Ftm_Gpt_Example_S32K144GPT
C:\NXP\S32DS.3.6.1\S32DS\software\PlatformSDK_S32K1_S32M24\RTD\Gpt_TS_T40D2M30I0R0\examples\S32DS\S32K1\Gpt_example_S32K144FPIT GPT
C:\NXP\S32DS.3.6.1\S32DS\software\PlatformSDK_S32K1_S32M24\RTD\Gpt_TS_T40D2M30I0R0\examples\S32DS\S32K1\Lpit_Gpt_Example_S32K144I²C
C:\NXP\S32DS.3.6.1\S32DS\software\PlatformSDK_S32K1_S32M24\RTD\I2c_TS_T40D2M30I0R0\examples\S32DS\S32K1\I2c_Example_S32K144I²C IP
C:\NXP\S32DS.3.6.1\S32DS\software\PlatformSDK_S32K1_S32M24\RTD\I2c_TS_T40D2M30I0R0\examples\S32DS\S32K1\I2c_Ip_Example_S32K144I²S leader
C:\NXP\S32DS.3.6.1\S32DS\software\PlatformSDK_S32K1_S32M24\RTD\I2s_TS_T40D2M30I0R0\examples\S32DS\S32K1\I2s_Flexio_to_Flexio_Example_Master_S32K144I²S follower
C:\NXP\S32DS.3.6.1\S32DS\software\PlatformSDK_S32K1_S32M24\RTD\I2s_TS_T40D2M30I0R0\examples\S32DS\S32K1\I2s_Flexio_to_Flexio_Example_Slave_S32K144I²S IP leader
C:\NXP\S32DS.3.6.1\S32DS\software\PlatformSDK_S32K1_S32M24\RTD\I2s_TS_T40D2M30I0R0\examples\S32DS\S32K1\I2s_Flexio_to_Flexio_Ip_example_Master_S32K144I²S IP follower
C:\NXP\S32DS.3.6.1\S32DS\software\PlatformSDK_S32K1_S32M24\RTD\I2s_TS_T40D2M30I0R0\examples\S32DS\S32K1\I2s_Flexio_to_Flexio_Ip_example_Slave_S32K144FTM ICU IP
C:\NXP\S32DS.3.6.1\S32DS\software\PlatformSDK_S32K1_S32M24\RTD\Icu_TS_T40D2M30I0R0\examples\S32DS\S32K1\Ftm_Icu_Ip_BlinkLed_S32K144ICU
C:\NXP\S32DS.3.6.1\S32DS\software\PlatformSDK_S32K1_S32M24\RTD\Icu_TS_T40D2M30I0R0\examples\S32DS\S32K1\Icu_BlinkLed_S32K144PORT CI ICU IP
C:\NXP\S32DS.3.6.1\S32DS\software\PlatformSDK_S32K1_S32M24\RTD\Icu_TS_T40D2M30I0R0\examples\S32DS\S32K1\Port_Ci_Icu_Ip_BlinkLed_S32K144LIN
C:\NXP\S32DS.3.6.1\S32DS\software\PlatformSDK_S32K1_S32M24\RTD\Lin_43_LPUART_FLEXIO_TS_T40D2M30I0R0\examples\S32DS\S32K1\Lin_Flexio_MasterFrameTransfer_S32K144LIN IP
C:\NXP\S32DS.3.6.1\S32DS\software\PlatformSDK_S32K1_S32M24\RTD\Lin_43_LPUART_FLEXIO_TS_T40D2M30I0R0\examples\S32DS\S32K1\Lin_Ip_FrameTransfer_S32K144LIN LPUART
C:\NXP\S32DS.3.6.1\S32DS\software\PlatformSDK_S32K1_S32M24\RTD\Lin_43_LPUART_FLEXIO_TS_T40D2M30I0R0\examples\S32DS\S32K1\Lin_Lpuart_MasterFrameTransfer_S32K144DMA IP
C:\NXP\S32DS.3.6.1\S32DS\software\PlatformSDK_S32K1_S32M24\RTD\Mcl_TS_T40D2M30I0R0\examples\S32DS\S32K1\Dma_Ip_DmaTransfer_S32K144MCL DMA
C:\NXP\S32DS.3.6.1\S32DS\software\PlatformSDK_S32K1_S32M24\RTD\Mcl_TS_T40D2M30I0R0\examples\S32DS\S32K1\Mcl_DmaTransfer_S32K144CLOCK IP
C:\NXP\S32DS.3.6.1\S32DS\software\PlatformSDK_S32K1_S32M24\RTD\Mcu_TS_T40D2M30I0R0\examples\S32DS\S32K1\Clock_Ip_Example_S32K144MCU
C:\NXP\S32DS.3.6.1\S32DS\software\PlatformSDK_S32K1_S32M24\RTD\Mcu_TS_T40D2M30I0R0\examples\S32DS\S32K1\Mcu_Example_S32K14POWER IP
C:\NXP\S32DS.3.6.1\S32DS\software\PlatformSDK_S32K1_S32M24\RTD\Mcu_TS_T40D2M30I0R0\examples\S32DS\S32K1\Power_Ip_Example_S32K144FTM OCU IP
C:\NXP\S32DS.3.6.1\S32DS\software\PlatformSDK_S32K1_S32M24\RTD\Ocu_TS_T40D2M30I0R0\examples\S32DS\S32K1\Ftm_Ocu_Ip_Example_S32K144OCU
C:\NXP\S32DS.3.6.1\S32DS\software\PlatformSDK_S32K1_S32M24\RTD\Ocu_TS_T40D2M30I0R0\examples\S32DS\S32K1\Ocu_Example_S32K144MPU IP
C:\NXP\S32DS.3.6.1\S32DS\software\PlatformSDK_S32K1_S32M24\RTD\Platform_TS_T40D2M30I0R0\examples\S32DS\S32K1\Mpu_Ip_Example_S32K144PLATFORM MPU HLD
C:\NXP\S32DS.3.6.1\S32DS\software\PlatformSDK_S32K1_S32M24\RTD\Platform_TS_T40D2M30I0R0\examples\S32DS\S32K1\Platform_Mpu_Hld_Example_S32K144PORT CI PORT IP
C:\NXP\S32DS.3.6.1\S32DS\software\PlatformSDK_S32K1_S32M24\RTD\Port_TS_T40D2M30I0R0\examples\S32DS\S32K1\Port_Ci_Port_Ip_Example_S32K144PORT
C:\NXP\S32DS.3.6.1\S32DS\software\PlatformSDK_S32K1_S32M24\RTD\Port_TS_T40D2M30I0R0\examples\S32DS\S32K1\Port_Example_S32K144FTM PWM IP
C:\NXP\S32DS.3.6.1\S32DS\software\PlatformSDK_S32K1_S32M24\RTD\Pwm_TS_T40D2M30I0R0\examples\S32DS\S32K1\Ftm_Pwm_Ip_Example_S32K144PWM
C:\NXP\S32DS.3.6.1\S32DS\software\PlatformSDK_S32K1_S32M24\RTD\Pwm_TS_T40D2M30I0R0\examples\S32DS\S32K1\Pwm_example_S32K144FTM QDEC IP
C:\NXP\S32DS.3.6.1\S32DS\software\PlatformSDK_S32K1_S32M24\RTD\Qdec_TS_T40D2M30I0R0\examples\S32DS\S32K1\Ftm_Qdec_Ip_Example_S32K144QDEC
C:\NXP\S32DS.3.6.1\S32DS\software\PlatformSDK_S32K1_S32M24\RTD\Qdec_TS_T40D2M30I0R0\examples\S32DS\S32K1\Qdec_Example_S32K144RM DMAMUX
C:\NXP\S32DS.3.6.1\S32DS\software\PlatformSDK_S32K1_S32M24\RTD\Rm_TS_T40D2M30I0R0\examples\S32DS\S32K1\Rm_DMAMUX_Example_S32K144LPSPI
C:\NXP\S32DS.3.6.1\S32DS\software\PlatformSDK_S32K1_S32M24\RTD\Spi_TS_T40D2M30I0R0\examples\S32DS\S32K1\Lpspi_Flexio_Ip_Transfer_S32K144LPSPI half-duplex
C:\NXP\S32DS.3.6.1\S32DS\software\PlatformSDK_S32K1_S32M24\RTD\Spi_TS_T40D2M30I0R0\examples\S32DS\S32K1\Lpspi_Ip_HalfDuplexTransfer_S32K144SPI half-duplex
C:\NXP\S32DS.3.6.1\S32DS\software\PlatformSDK_S32K1_S32M24\RTD\Spi_TS_T40D2M30I0R0\examples\S32DS\S32K1\Spi_HalfDuplexTransfer_S32K144SPI
C:\NXP\S32DS.3.6.1\S32DS\software\PlatformSDK_S32K1_S32M24\RTD\Spi_TS_T40D2M30I0R0\examples\S32DS\S32K1\Spi_Transfer_S32K144LPUART
C:\NXP\S32DS.3.6.1\S32DS\software\PlatformSDK_S32K1_S32M24\RTD\Uart_TS_T40D2M30I0R0\examples\S32DS\S32K1\LpuartFlexio_Uart_Ip_Example_S32K144UART
C:\NXP\S32DS.3.6.1\S32DS\software\PlatformSDK_S32K1_S32M24\RTD\Uart_TS_T40D2M30I0R0\examples\S32DS\S32K1\Uart_Example_S32K144WDOG
C:\NXP\S32DS.3.6.1\S32DS\software\PlatformSDK_S32K1_S32M24\RTD\Wdg_TS_T40D2M30I0R0\examples\S32DS\S32K1\Wdg_Example_S32K144WDOG EWM IP
C:\NXP\S32DS.3.6.1\S32DS\software\PlatformSDK_S32K1_S32M24\RTD\Wdg_TS_T40D2M30I0R0\examples\S32DS\S32K1\Wdog_Ewm_Ip_Example_S32K144Design Resources
Board Assets
Chip Assets
Support
Forums
Connect with other engineers and get expert advice on designing with the S32K144EVB on one of our community sites.
On this page
- 1.1
Get to Know Your Evaluation Board
- 1.2
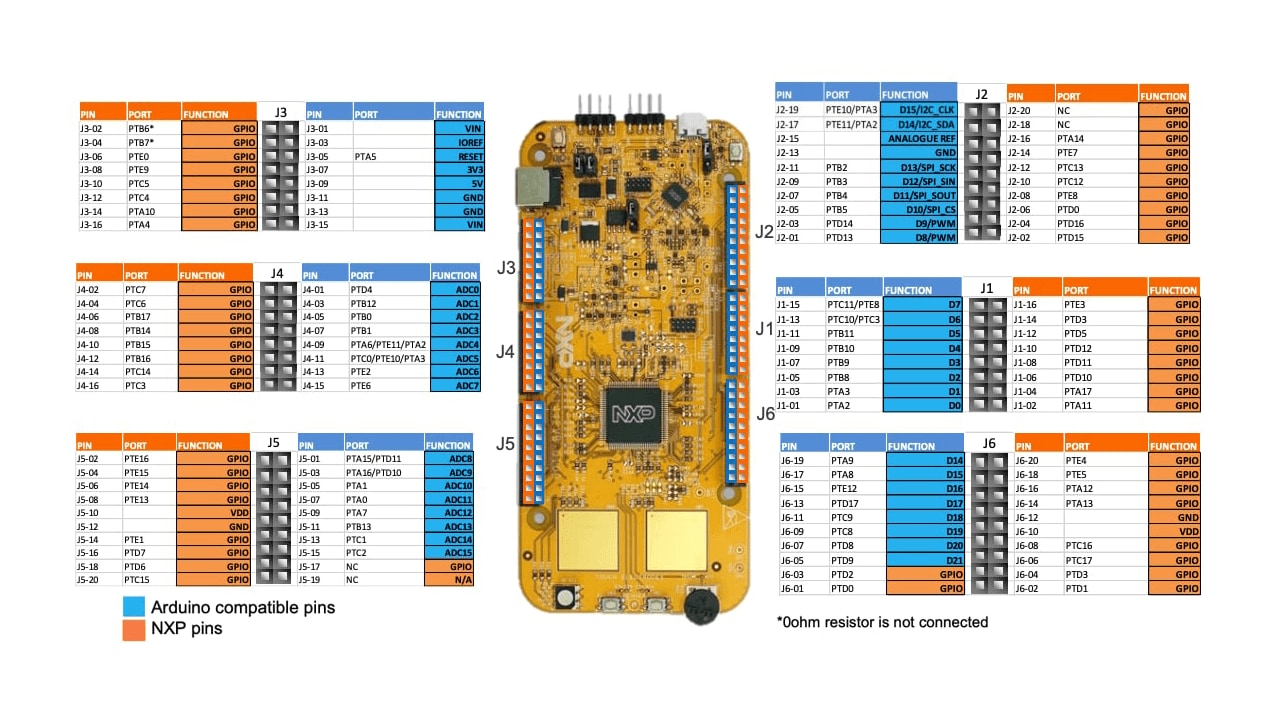
Understanding the Header/Pinout
- 1.3
Understanding the HMI Mapping
- 4.1
Communicate with Run-Time Debugger
- 4.2
FreeMASTER JumpStart Project Loaded
- 4.3
Import and Debug the Project to IDE
- 4.4
Set Up Debug Configuration